课设有个选题是巩固Linux网络协议栈,刚好最近再看Linux源码,就想试试能不能写出来,以Linux 4.9 TCP协议 IPv4 为例开始分析。
初始化
为了排版好看点,把初始化放在前面,在后续用到的时候再来看
net_families
关于net_families数组,该数值是在调用sock_register函数初始化的
sock_register函数
int sock_register(const struct net_proto_family *ops)
{
int err;
if (ops->family >= NPROTO) {
pr_crit("protocol %d >= NPROTO(%d)\n", ops->family, NPROTO);
return -ENOBUFS;
}
spin_lock(&net_family_lock);
if (rcu_dereference_protected(net_families[ops->family],
lockdep_is_held(&net_family_lock)))
err = -EEXIST;
else {
rcu_assign_pointer(net_families[ops->family], ops);
err = 0;
}
spin_unlock(&net_family_lock);
pr_info("NET: Registered protocol family %d\n", ops->family);
return err;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(sock_register);简化后
int sock_register(const struct net_proto_family *ops)
{
...................
rcu_assign_pointer(net_families[ops->family], ops);
...................
}实现了net_families[ops->family]=ops,而在/net/ipv4/af_inet.c中注册了inet_family_ops
static int __init inet_init(void)
{
.........................
(void)sock_register(&inet_family_ops);
.........................
}inet_family_ops结构体如下
#define PF_INET AF_INET
static const struct net_proto_family inet_family_ops = {
.family = PF_INET,
.create = inet_create,
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
};inetsw
sock_register函数中遍历inetsw_array数组并执行inet_register_protosw函数。
int sock_register(const struct net_proto_family *ops)
{
...................
for (q = inetsw_array; q < &inetsw_array[INETSW_ARRAY_LEN]; ++q)
inet_register_protosw(q);
...................
}inetsw_array数组如下,里面的成员都是inet_protosw类型的。
static struct inet_protosw inetsw_array[] =
{
{
.type = SOCK_STREAM,
.protocol = IPPROTO_TCP,
.prot = &tcp_prot,
.ops = &inet_stream_ops,
.flags = INET_PROTOSW_PERMANENT |
INET_PROTOSW_ICSK,
},
{
.type = SOCK_DGRAM,
.protocol = IPPROTO_UDP,
.prot = &udp_prot,
.ops = &inet_dgram_ops,
.flags = INET_PROTOSW_PERMANENT,
},
{
.type = SOCK_DGRAM,
.protocol = IPPROTO_ICMP,
.prot = &ping_prot,
.ops = &inet_sockraw_ops,
.flags = INET_PROTOSW_REUSE,
},
{
.type = SOCK_RAW,
.protocol = IPPROTO_IP, /* wild card */
.prot = &raw_prot,
.ops = &inet_sockraw_ops,
.flags = INET_PROTOSW_REUSE,
}
};inet_register_protosw函数
static struct list_head inetsw[SOCK_MAX];
void inet_register_protosw(struct inet_protosw *p)
{
struct list_head *lh;
struct inet_protosw *answer;
int protocol = p->protocol;
struct list_head *last_perm;
last_perm = &inetsw[p->type];
list_for_each(lh, &inetsw[p->type]) {
answer = list_entry(lh, struct inet_protosw, list);
if (protocol == answer->protocol)
goto out_permanent;
last_perm = lh;
}
return;
list_add_rcu(&p->list, last_perm);
}inetsw数组的成员类型为list_head即数组里装的是头节点。inet_protosw 结构体内部有指向下一个inet_protosw结构体的指针,遍历当前type的链表,将每个inet_protosw节点赋值给answer。
struct inet_protosw {
struct list_head list;
..........................
};
answer = list_entry(lh, struct inet_protosw, list);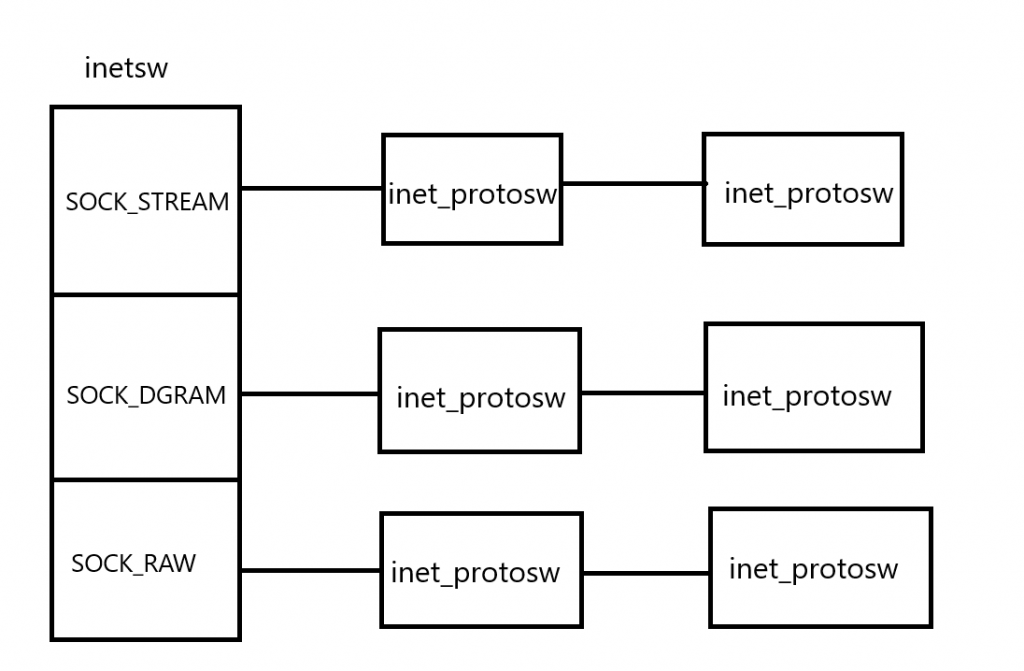
判断协议的名字是否重复
if (protocol == answer->protocol)
goto out_permanent;将该inet_protosw结构体插入list中
list_add_rcu(&p->list, last_perm);sock
sk_alloc创建了一个sock结构体以供操作系统使用
sk = sk_alloc(net, PF_INET, GFP_KERNEL, answer_prot, kern);
struct sock *sk_alloc(struct net *net, int family, gfp_t priority,
struct proto *prot, int kern)
{
struct sock *sk;
sk = sk_prot_alloc(prot, priority | __GFP_ZERO, family);
if (sk) {
sk->sk_family = family;
sk->sk_prot = sk->sk_prot_creator = prot;
sock_lock_init(sk);
sk->sk_net_refcnt = kern ? 0 : 1;
}
return sk;
}在sk_alloc函数中sk_prot_alloc创建了一个sock结构体,在后续我们会经常使用他,通过结构体嵌套在C语言中实现了C++的多态和继承功能,在后面中会讲到
在sk_alloc函数和inet_create后续中实现了,最重要的还是前两条
- sk->sk_family = PF_INET
- sk->sk_prot = sk->sk_prot_creator = answer_prot=tcp_prot
- sk->sk_destruct = inet_sock_destruct;
- sk->sk_protocol = protocol
- sk->sk_backlog_rcv = sk->sk_prot->backlog_rcv;
sock是最基本的结构体也就是父类,在其之下有很多子类
inet_sock
struct inet_sock {
/* sk and pinet6 has to be the first two members of inet_sock */
struct sock sk;
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_IPV6)
struct ipv6_pinfo *pinet6;
#endif
/* Socket demultiplex comparisons on incoming packets. */
#define inet_daddr sk.__sk_common.skc_daddr
#define inet_rcv_saddr sk.__sk_common.skc_rcv_saddr
#define inet_dport sk.__sk_common.skc_dport
#define inet_num sk.__sk_common.skc_num
unsigned long inet_flags;
__be32 inet_saddr;
__s16 uc_ttl;
__be16 inet_sport;
struct ip_options_rcu __rcu *inet_opt;
atomic_t inet_id;
__u8 tos;
__u8 min_ttl;
__u8 mc_ttl;
__u8 pmtudisc;
__u8 rcv_tos;
__u8 convert_csum;
int uc_index;
int mc_index;
__be32 mc_addr;
u32 local_port_range; /* high << 16 | low */
struct ip_mc_socklist __rcu *mc_list;
struct inet_cork_full cork;
};
#define IPCORK_OPT 1 /* ip-options has been held in ipcork.opt */
#define IPCORK_TS_OPT_ID 2 /* ts_opt_id field is valid, overriding sk_tskey */
enum {
INET_FLAGS_PKTINFO = 0,
INET_FLAGS_TTL = 1,
INET_FLAGS_TOS = 2,
INET_FLAGS_RECVOPTS = 3,
INET_FLAGS_RETOPTS = 4,
INET_FLAGS_PASSSEC = 5,
INET_FLAGS_ORIGDSTADDR = 6,
INET_FLAGS_CHECKSUM = 7,
INET_FLAGS_RECVFRAGSIZE = 8,
INET_FLAGS_RECVERR = 9,
INET_FLAGS_RECVERR_RFC4884 = 10,
INET_FLAGS_FREEBIND = 11,
INET_FLAGS_HDRINCL = 12,
INET_FLAGS_MC_LOOP = 13,
INET_FLAGS_MC_ALL = 14,
INET_FLAGS_TRANSPARENT = 15,
INET_FLAGS_IS_ICSK = 16,
INET_FLAGS_NODEFRAG = 17,
INET_FLAGS_BIND_ADDRESS_NO_PORT = 18,
INET_FLAGS_DEFER_CONNECT = 19,
INET_FLAGS_MC6_LOOP = 20,
INET_FLAGS_RECVERR6_RFC4884 = 21,
INET_FLAGS_MC6_ALL = 22,
INET_FLAGS_AUTOFLOWLABEL_SET = 23,
INET_FLAGS_AUTOFLOWLABEL = 24,
INET_FLAGS_DONTFRAG = 25,
INET_FLAGS_RECVERR6 = 26,
INET_FLAGS_REPFLOW = 27,
INET_FLAGS_RTALERT_ISOLATE = 28,
INET_FLAGS_SNDFLOW = 29,
INET_FLAGS_RTALERT = 30,
};inet_connect_sock
struct inet_connection_sock {
/* inet_sock has to be the first member! */
struct inet_sock icsk_inet;
struct request_sock_queue icsk_accept_queue;
struct inet_bind_bucket *icsk_bind_hash;
unsigned long icsk_timeout;
struct timer_list icsk_retransmit_timer;
struct timer_list icsk_delack_timer;
__u32 icsk_rto;
__u32 icsk_pmtu_cookie;
const struct tcp_congestion_ops *icsk_ca_ops;
const struct inet_connection_sock_af_ops *icsk_af_ops;
unsigned int (*icsk_sync_mss)(struct sock *sk, u32 pmtu);
__u8 icsk_ca_state:6,
icsk_ca_setsockopt:1,
icsk_ca_dst_locked:1;
__u8 icsk_retransmits;
__u8 icsk_pending;
__u8 icsk_backoff;
__u8 icsk_syn_retries;
__u8 icsk_probes_out;
__u16 icsk_ext_hdr_len;
struct {
__u8 pending; /* ACK is pending */
__u8 quick; /* Scheduled number of quick acks */
__u8 pingpong; /* The session is interactive */
__u8 blocked; /* Delayed ACK was blocked by socket lock */
__u32 ato; /* Predicted tick of soft clock */
unsigned long timeout; /* Currently scheduled timeout */
__u32 lrcvtime; /* timestamp of last received data packet */
__u16 last_seg_size; /* Size of last incoming segment */
__u16 rcv_mss; /* MSS used for delayed ACK decisions */
} icsk_ack;
struct {
int enabled;
/* Range of MTUs to search */
int search_high;
int search_low;
/* Information on the current probe. */
int probe_size;
u32 probe_timestamp;
} icsk_mtup;
u32 icsk_user_timeout;
u64 icsk_ca_priv[88 / sizeof(u64)];
#define ICSK_CA_PRIV_SIZE (11 * sizeof(u64))
};tcp_sock
struct tcp_sock {
/* inet_connection_sock has to be the first member of tcp_sock */
struct inet_connection_sock inet_conn;
u16 tcp_header_len; /* Bytes of tcp header to send */
u16 gso_segs; /* Max number of segs per GSO packet */
/*
* Header prediction flags
* 0x5?10 << 16 + snd_wnd in net byte order
*/
__be32 pred_flags;
/*
* RFC793 variables by their proper names. This means you can
* read the code and the spec side by side (and laugh ...)
* See RFC793 and RFC1122. The RFC writes these in capitals.
*/
u64 bytes_received; /* RFC4898 tcpEStatsAppHCThruOctetsReceived
* sum(delta(rcv_nxt)), or how many bytes
* were acked.
*/
u32 segs_in; /* RFC4898 tcpEStatsPerfSegsIn
* total number of segments in.
*/
u32 data_segs_in; /* RFC4898 tcpEStatsPerfDataSegsIn
* total number of data segments in.
*/
u32 rcv_nxt; /* What we want to receive next */
u32 copied_seq; /* Head of yet unread data */
u32 rcv_wup; /* rcv_nxt on last window update sent */
u32 snd_nxt; /* Next sequence we send */
u32 segs_out; /* RFC4898 tcpEStatsPerfSegsOut
* The total number of segments sent.
*/
u32 data_segs_out; /* RFC4898 tcpEStatsPerfDataSegsOut
* total number of data segments sent.
*/
u64 bytes_acked; /* RFC4898 tcpEStatsAppHCThruOctetsAcked
* sum(delta(snd_una)), or how many bytes
* were acked.
*/
struct u64_stats_sync syncp; /* protects 64bit vars (cf tcp_get_info()) */
u32 snd_una; /* First byte we want an ack for */
u32 snd_sml; /* Last byte of the most recently transmitted small packet */
u32 rcv_tstamp; /* timestamp of last received ACK (for keepalives) */
u32 lsndtime; /* timestamp of last sent data packet (for restart window) */
u32 last_oow_ack_time; /* timestamp of last out-of-window ACK */
u32 tsoffset; /* timestamp offset */
struct list_head tsq_node; /* anchor in tsq_tasklet.head list */
unsigned long tsq_flags;
/* Data for direct copy to user */
struct {
struct sk_buff_head prequeue;
struct task_struct *task;
struct msghdr *msg;
int memory;
int len;
} ucopy;
u32 snd_wl1; /* Sequence for window update */
u32 snd_wnd; /* The window we expect to receive */
u32 max_window; /* Maximal window ever seen from peer */
u32 mss_cache; /* Cached effective mss, not including SACKS */
u32 window_clamp; /* Maximal window to advertise */
u32 rcv_ssthresh; /* Current window clamp */
/* Information of the most recently (s)acked skb */
struct tcp_rack {
struct skb_mstamp mstamp; /* (Re)sent time of the skb */
u8 advanced; /* mstamp advanced since last lost marking */
u8 reord; /* reordering detected */
} rack;
u16 advmss; /* Advertised MSS */
u8 tlp_retrans:1, /* TLP is a retransmission */
unused_1:7;
u8 rate_app_limited:1, /* rate_{delivered,interval_us} limited? */
is_sack_reneg:1, /* in recovery from loss with SACK reneg? */
unused:6;
u8 nonagle : 4,/* Disable Nagle algorithm? */
thin_lto : 1,/* Use linear timeouts for thin streams */
thin_dupack : 1,/* Fast retransmit on first dupack */
repair : 1,
frto : 1;/* F-RTO (RFC5682) activated in CA_Loss */
u8 repair_queue;
u8 do_early_retrans:1,/* Enable RFC5827 early-retransmit */
syn_data:1, /* SYN includes data */
syn_fastopen:1, /* SYN includes Fast Open option */
syn_fastopen_exp:1,/* SYN includes Fast Open exp. option */
syn_data_acked:1,/* data in SYN is acked by SYN-ACK */
save_syn:1, /* Save headers of SYN packet */
is_cwnd_limited:1;/* forward progress limited by snd_cwnd? */
u32 tlp_high_seq; /* snd_nxt at the time of TLP */
/* RTT measurement */
u32 srtt_us; /* smoothed round trip time << 3 in usecs */
u32 mdev_us; /* medium deviation */
u32 mdev_max_us; /* maximal mdev for the last rtt period */
u32 rttvar_us; /* smoothed mdev_max */
u32 rtt_seq; /* sequence number to update rttvar */
struct minmax rtt_min;
u32 packets_out; /* Packets which are "in flight" */
u32 retrans_out; /* Retransmitted packets out */
u32 max_packets_out; /* max packets_out in last window */
u32 cwnd_usage_seq; /* right edge of cwnd usage tracking flight */
u16 urg_data; /* Saved octet of OOB data and control flags */
u8 ecn_flags; /* ECN status bits. */
u8 keepalive_probes; /* num of allowed keep alive probes */
u32 reordering; /* Packet reordering metric. */
u32 snd_up; /* Urgent pointer */
/*
* Options received (usually on last packet, some only on SYN packets).
*/
struct tcp_options_received rx_opt;
/*
* Slow start and congestion control (see also Nagle, and Karn & Partridge)
*/
u32 snd_ssthresh; /* Slow start size threshold */
u32 snd_cwnd; /* Sending congestion window */
u32 snd_cwnd_cnt; /* Linear increase counter */
u32 snd_cwnd_clamp; /* Do not allow snd_cwnd to grow above this */
u32 snd_cwnd_used;
u32 snd_cwnd_stamp;
u32 prior_cwnd; /* Congestion window at start of Recovery. */
u32 prr_delivered; /* Number of newly delivered packets to
* receiver in Recovery. */
u32 prr_out; /* Total number of pkts sent during Recovery. */
u32 delivered; /* Total data packets delivered incl. rexmits */
u32 lost; /* Total data packets lost incl. rexmits */
u32 app_limited; /* limited until "delivered" reaches this val */
struct skb_mstamp first_tx_mstamp; /* start of window send phase */
struct skb_mstamp delivered_mstamp; /* time we reached "delivered" */
u32 rate_delivered; /* saved rate sample: packets delivered */
u32 rate_interval_us; /* saved rate sample: time elapsed */
u32 rcv_wnd; /* Current receiver window */
u32 write_seq; /* Tail(+1) of data held in tcp send buffer */
u32 notsent_lowat; /* TCP_NOTSENT_LOWAT */
u32 pushed_seq; /* Last pushed seq, required to talk to windows */
u32 lost_out; /* Lost packets */
u32 sacked_out; /* SACK'd packets */
u32 fackets_out; /* FACK'd packets */
/* from STCP, retrans queue hinting */
struct sk_buff* lost_skb_hint;
struct sk_buff *retransmit_skb_hint;
/* OOO segments go in this rbtree. Socket lock must be held. */
struct rb_root out_of_order_queue;
struct sk_buff *ooo_last_skb; /* cache rb_last(out_of_order_queue) */
/* SACKs data, these 2 need to be together (see tcp_options_write) */
struct tcp_sack_block duplicate_sack[1]; /* D-SACK block */
struct tcp_sack_block selective_acks[4]; /* The SACKS themselves*/
struct tcp_sack_block recv_sack_cache[4];
struct sk_buff *highest_sack; /* skb just after the highest
* skb with SACKed bit set
* (validity guaranteed only if
* sacked_out > 0)
*/
int lost_cnt_hint;
u32 retransmit_high; /* L-bits may be on up to this seqno */
u32 prior_ssthresh; /* ssthresh saved at recovery start */
u32 high_seq; /* snd_nxt at onset of congestion */
u32 retrans_stamp; /* Timestamp of the last retransmit,
* also used in SYN-SENT to remember stamp of
* the first SYN. */
u32 undo_marker; /* snd_una upon a new recovery episode. */
int undo_retrans; /* number of undoable retransmissions. */
u32 total_retrans; /* Total retransmits for entire connection */
u32 urg_seq; /* Seq of received urgent pointer */
unsigned int keepalive_time; /* time before keep alive takes place */
unsigned int keepalive_intvl; /* time interval between keep alive probes */
int linger2;
/* Receiver side RTT estimation */
struct {
u32 rtt;
u32 seq;
u32 time;
} rcv_rtt_est;
/* Receiver queue space */
struct {
u32 space;
u32 seq;
u32 time;
} rcvq_space;
/* TCP-specific MTU probe information. */
struct {
u32 probe_seq_start;
u32 probe_seq_end;
} mtu_probe;
u32 mtu_info; /* We received an ICMP_FRAG_NEEDED / ICMPV6_PKT_TOOBIG
* while socket was owned by user.
*/
#ifdef CONFIG_TCP_MD5SIG
/* TCP AF-Specific parts; only used by MD5 Signature support so far */
const struct tcp_sock_af_ops *af_specific;
/* TCP MD5 Signature Option information */
struct tcp_md5sig_info __rcu *md5sig_info;
#endif
/* TCP fastopen related information */
struct tcp_fastopen_request *fastopen_req;
/* fastopen_rsk points to request_sock that resulted in this big
* socket. Used to retransmit SYNACKs etc.
*/
struct request_sock *fastopen_rsk;
u32 *saved_syn;
};
我们可以看到tcp_sock嵌套inet_connect_sock结构体,而inet_connect_sock又嵌套了inet_sock结构体,inet_sock嵌套了sock结构体,实现了一种结构体嵌套达到了C++的继承特性。
在sk_alloc中调用了sk_prot_alloc为sock结构体分配空间,其中sk_prot_alloc函数调用了kmalloc,用tcp->slab进行sock结构体的创建
static struct sock *sk_prot_alloc(struct proto *prot, gfp_t priority,int family)
{
struct sock *sk;
struct kmem_cache *slab;
slab = prot->slab;
sk = kmem_cache_alloc(slab, priority & ~__GFP_ZERO);
}prot->slab的初始化在proto_register函数中的
int proto_register(struct proto *prot, int alloc_slab)
{
if (alloc_slab) {
prot->slab = kmem_cache_create(prot->name, prot->obj_size, 0,
SLAB_HWCACHE_ALIGN | prot->slab_flags,
NULL);
......................................
}slab的大小由prot->obj_size确定,如下图prot->obj_size=sizeof(tcp_sock)
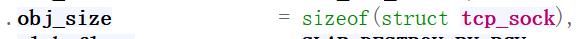
由此可见我们执行sk_alloc创建sock结构体时并不是开辟一个sock结构体的空间,而是tcp_sock结构体的空间。
所以之后我们所见的各种指针转换都是基于此基础上的
struct inet_sock *inet = inet_sk(sk);
struct inet_connection_sock *icsk = inet_csk(sk);
struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk);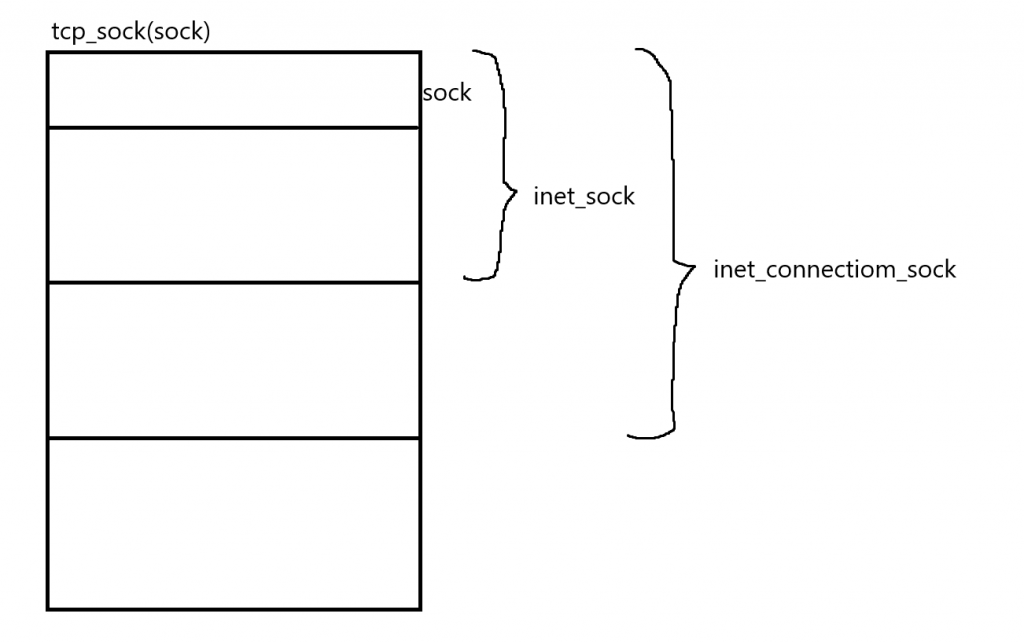
由于我们得到的sock在最顶层和tcp_sock地址相同,我们可以通过指针转换来访问同一个sock的子类
icsk->icsk_af_ops
icsk->icsk_af_ops的初始化在tcp_v4_init_sock函数中完成,而tcp_v4_init_sock函数是在tcp_prot中,在inet_create函数中调用的tcp_v4_init_sock。
struct proto tcp_prot = {
.init = tcp_v4_init_sock,
}
inet_create:
if (sk->sk_prot->init) {
err = sk->sk_prot->init(sk);
if (err)
sk_common_release(sk);
}tcp_v4_init_sock代码如下,icsk->icsk_af_ops被赋值了ipv4_specific
static int tcp_v4_init_sock(struct sock *sk)
{
struct inet_connection_sock *icsk = inet_csk(sk);
tcp_init_sock(sk);
icsk->icsk_af_ops = &ipv4_specific;
return 0;
}ipv4_specific
const struct inet_connection_sock_af_ops ipv4_specific = {
.queue_xmit = ip_queue_xmit,
.send_check = tcp_v4_send_check,
.rebuild_header = inet_sk_rebuild_header,
.sk_rx_dst_set = inet_sk_rx_dst_set,
.conn_request = tcp_v4_conn_request,
.syn_recv_sock = tcp_v4_syn_recv_sock,
.net_header_len = sizeof(struct iphdr),
.setsockopt = ip_setsockopt,
.getsockopt = ip_getsockopt,
.addr2sockaddr = inet_csk_addr2sockaddr,
.sockaddr_len = sizeof(struct sockaddr_in),
.bind_conflict = inet_csk_bind_conflict,
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
.compat_setsockopt = compat_ip_setsockopt,
.compat_getsockopt = compat_ip_getsockopt,
#endif
.mtu_reduced = tcp_v4_mtu_reduced,
};必要知识
该模块介绍某些结构体和通用的操作。。。。。
inet_hashinfo
inet_hashinfo结构体专门用来放置连接信息的,inet_hashinfo结构体如下,只截取了关键成员
struct inet_hashinfo {
struct inet_ehash_bucket *ehash;
struct inet_bind_hashbucket *bhash;
struct inet_listen_hashbucket listening_hash[INET_LHTABLE_SIZE]
};- ehash(estblished hash):用于存放完整连接信息的字典,{{saddr,daddr,sport,dport}:sock}
- bhash(bind hash):用于存放绑定某端口号的连接的字典。{port:sock}
- listening_hash:用于存放处于监听状态下的sock的字典,{port:sock}
bhash
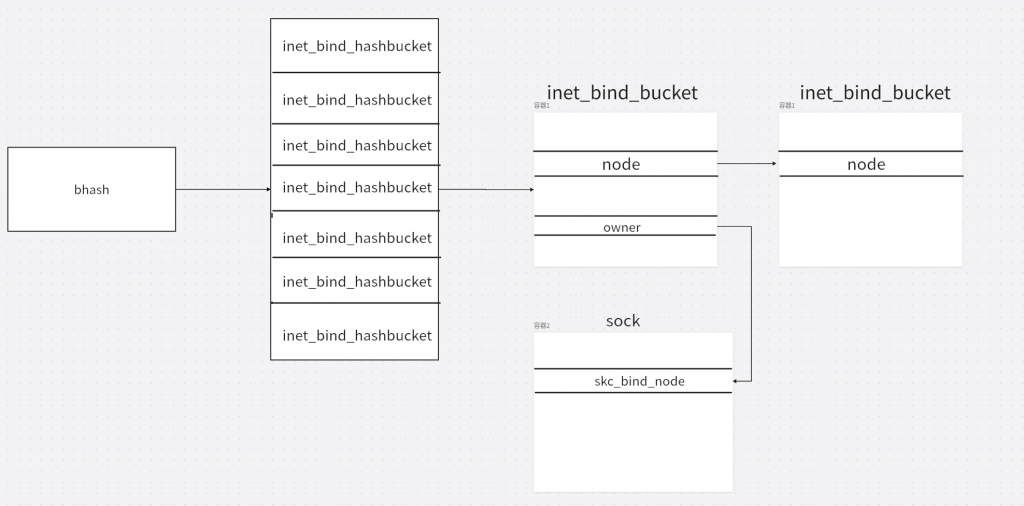
bhash的类型是一个inet_bind_hashbucket结构体,结构体如下
struct inet_bind_hashbucket {
spinlock_t lock;
struct hlist_head chain;
};bhash用来存储数据的结构体叫做inet_bind_bucket,里面记录了绑定的端口号(port),拥有者(owners)和用于将每个inet_bind_bucket作为连接起来的node。
struct inet_bind_bucket {
possible_net_t ib_net;
unsigned short port;
signed char fastreuse;
signed char fastreuseport;
kuid_t fastuid;
int num_owners;
struct hlist_node node;
struct hlist_head owners;
};在sock结构体里有个sock_common结构体,里面存储着skc_bind_node/skc_portaddr_node成员,inet_bind_bucket结构体中的owners成员就指向它。
struct sock_common
{
......................
union {
struct hlist_node skc_bind_node;
struct hlist_node skc_portaddr_node;
};
......................
}
listening_hash
和bindhash相同有两个成员
struct inet_listen_hashbucket {
spinlock_t lock;
union {
struct hlist_head head;
struct hlist_nulls_head nulls_head;
};
};nulls_head指向sock结构体的sock_common中的skc_nulls_node/skc_nulls_node
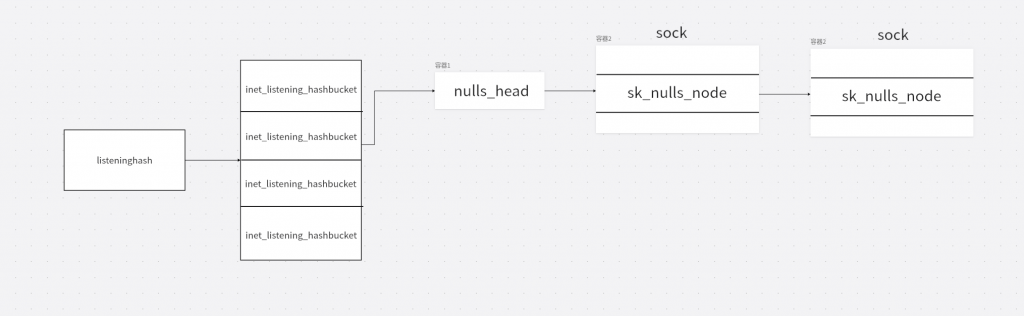
ehash
ehash指向一个inet_ehash_bucket的数组,inet_ehash_bucket 结构体如下,只有一个成员。
struct inet_ehash_bucket {
struct hlist_nulls_head chain;
};chain指向sock结构体的sock_common中的skc_nulls_node/skc_nulls_node
union {
struct hlist_node skc_node;
struct hlist_nulls_node skc_nulls_node;
};sock结构体的状态
在sock结构体里存在一个成员来表示当前sock的状态
#define sk_state __sk_common.skc_statesock总共有以下几个状态
enum {
TCPF_ESTABLISHED = (1 << 1),
TCPF_SYN_SENT = (1 << 2),
TCPF_SYN_RECV = (1 << 3),
TCPF_FIN_WAIT1 = (1 << 4),
TCPF_FIN_WAIT2 = (1 << 5),
TCPF_TIME_WAIT = (1 << 6),
TCPF_CLOSE = (1 << 7),
TCPF_CLOSE_WAIT = (1 << 8),
TCPF_LAST_ACK = (1 << 9),
TCPF_LISTEN = (1 << 10),
TCPF_CLOSING = (1 << 11),
TCPF_NEW_SYN_RECV = (1 << 12),
};socket有以下几个状态
typedef enum {
SS_FREE = 0, /* not allocated */
SS_UNCONNECTED, /* unconnected to any socket */
SS_CONNECTING, /* in process of connecting */
SS_CONNECTED, /* connected to socket */
SS_DISCONNECTING /* in process of disconnecting */
} socket_state;当要检查sock结构体状态时通常采用以下代码
if (!((1 << old_state) & (TCPF_CLOSE | TCPF_LISTEN)))
goto out;用(1<<state)& (TCPF_LISTEN|TCPF_CLOSE )就可以判断当前状态是否在两个之间。若在这些状态之间,则相与不为0,反之为0.
#TCPF_LISTEN
(10000000000&10001000000)=10000000000
#TCPF_CLOSE
(00001000000&10001000000)=00001000000sk_buff
sk_buff是Linux网络协议栈中用于管理和控制接收或发送数据包的关键数据结构。结构体如下
sk_buff
struct sk_buff {
union {
struct {
/* These two members must be first. */
struct sk_buff *next;
struct sk_buff *prev;
union {
ktime_t tstamp;
struct skb_mstamp skb_mstamp;
};
};
struct rb_node rbnode; /* used in netem, ip4 defrag, and tcp stack */
};
union {
struct sock *sk;
int ip_defrag_offset;
};
struct net_device *dev;
/*
* This is the control buffer. It is free to use for every
* layer. Please put your private variables there. If you
* want to keep them across layers you have to do a skb_clone()
* first. This is owned by whoever has the skb queued ATM.
*/
char cb[48] __aligned(8);
unsigned long _skb_refdst;
void (*destructor)(struct sk_buff *skb);
#ifdef CONFIG_XFRM
struct sec_path *sp;
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_NF_CONNTRACK) || defined(CONFIG_NF_CONNTRACK_MODULE)
struct nf_conntrack *nfct;
#endif
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_BRIDGE_NETFILTER)
struct nf_bridge_info *nf_bridge;
#endif
unsigned int len,
data_len;
__u16 mac_len,
hdr_len;
/* Following fields are _not_ copied in __copy_skb_header()
* Note that queue_mapping is here mostly to fill a hole.
*/
kmemcheck_bitfield_begin(flags1);
__u16 queue_mapping;
/* if you move cloned around you also must adapt those constants */
#ifdef __BIG_ENDIAN_BITFIELD
#define CLONED_MASK (1 << 7)
#else
#define CLONED_MASK 1
#endif
#define CLONED_OFFSET() offsetof(struct sk_buff, __cloned_offset)
__u8 __cloned_offset[0];
__u8 cloned:1,
nohdr:1,
fclone:2,
peeked:1,
head_frag:1,
xmit_more:1,
pfmemalloc:1;
kmemcheck_bitfield_end(flags1);
/* fields enclosed in headers_start/headers_end are copied
* using a single memcpy() in __copy_skb_header()
*/
/* private: */
__u32 headers_start[0];
/* public: */
/* if you move pkt_type around you also must adapt those constants */
#ifdef __BIG_ENDIAN_BITFIELD
#define PKT_TYPE_MAX (7 << 5)
#else
#define PKT_TYPE_MAX 7
#endif
#define PKT_TYPE_OFFSET() offsetof(struct sk_buff, __pkt_type_offset)
__u8 __pkt_type_offset[0];
__u8 pkt_type:3;
__u8 ignore_df:1;
__u8 nfctinfo:3;
__u8 nf_trace:1;
__u8 ip_summed:2;
__u8 ooo_okay:1;
__u8 l4_hash:1;
__u8 sw_hash:1;
__u8 wifi_acked_valid:1;
__u8 wifi_acked:1;
__u8 no_fcs:1;
/* Indicates the inner headers are valid in the skbuff. */
__u8 encapsulation:1;
__u8 encap_hdr_csum:1;
__u8 csum_valid:1;
__u8 csum_complete_sw:1;
__u8 csum_level:2;
__u8 csum_bad:1;
#ifdef CONFIG_IPV6_NDISC_NODETYPE
__u8 ndisc_nodetype:2;
#endif
__u8 ipvs_property:1;
__u8 inner_protocol_type:1;
__u8 remcsum_offload:1;
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_SWITCHDEV
__u8 offload_fwd_mark:1;
#endif
/* 2, 4 or 5 bit hole */
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_SCHED
__u16 tc_index; /* traffic control index */
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_CLS_ACT
__u16 tc_verd; /* traffic control verdict */
#endif
#endif
union {
__wsum csum;
struct {
__u16 csum_start;
__u16 csum_offset;
};
};
__u32 priority;
int skb_iif;
__u32 hash;
__be16 vlan_proto;
__u16 vlan_tci;
#if defined(CONFIG_NET_RX_BUSY_POLL) || defined(CONFIG_XPS)
union {
unsigned int napi_id;
unsigned int sender_cpu;
};
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NETWORK_SECMARK
__u32 secmark;
#endif
union {
__u32 mark;
__u32 reserved_tailroom;
};
union {
__be16 inner_protocol;
__u8 inner_ipproto;
};
__u16 inner_transport_header;
__u16 inner_network_header;
__u16 inner_mac_header;
__be16 protocol;
__u16 transport_header;
__u16 network_header;
__u16 mac_header;
/* private: */
__u32 headers_end[0];
/* public: */
/* These elements must be at the end, see alloc_skb() for details. */
sk_buff_data_t tail;
sk_buff_data_t end;
unsigned char *head,
*data;
unsigned int truesize;
atomic_t users;
};在sk_buff中有几个重要成员,为了让作用差不多的成员放在一起故打乱了成员的顺序。
struct sk_buff {
char cb[48] __aligned(8);
unsigned int len;
unsigned int data_len;
__be16 protocol;
__u16 transport_header;
__u16 network_header;
__u16 mac_header;
unsigned int truesize;
sk_buff_data_t tail;
sk_buff_data_t end;
unsigned char *head,
*data;
};- cb:控制块,用于存放各层的控制数据
- len:表示当前skb数据区的长度
- data_len:实际存放数据的大小
- truesize:表示整个sk_buff所占用的大小,包括sk_buff结构体大小,数据区大小,以及skb_shared_info结构体和内存对齐的大小。
- protocol:当前的协议
- transport_header,network_header,mac_header:数据区到各层头部的偏移
- tail:指向存放各层数据的尾部
- end:指向数据区的尾部
- head:指向数据区的头部
- data:指向存放各层数据的头部
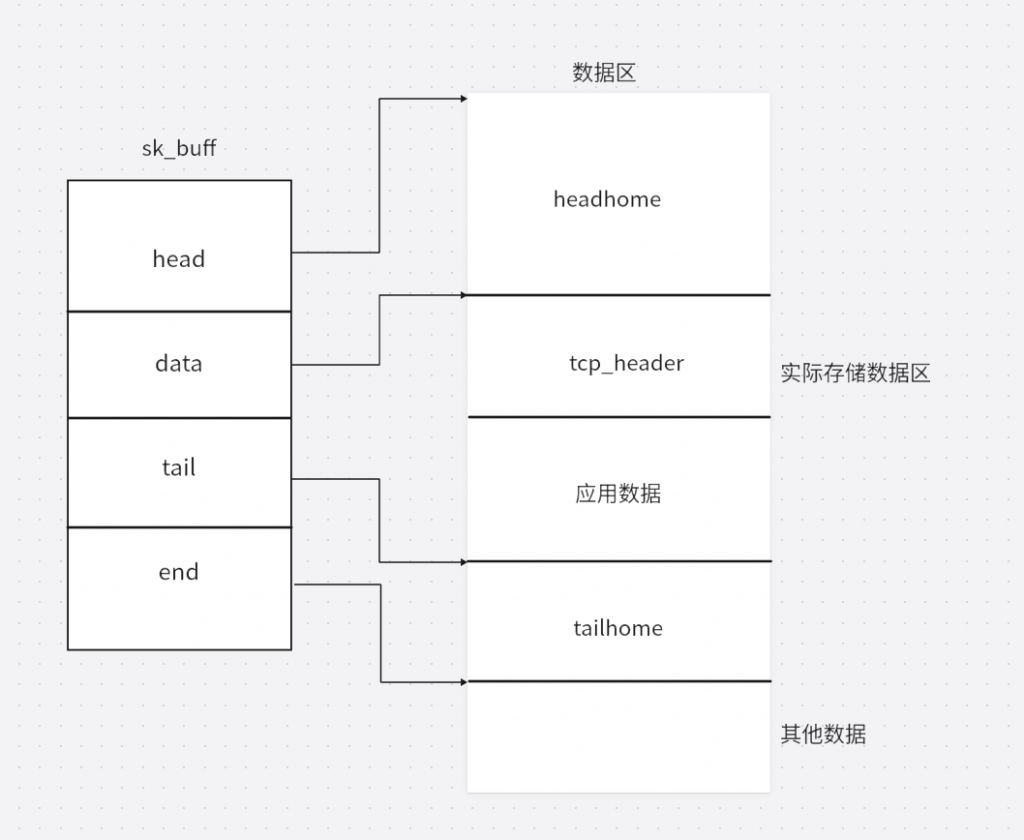
在sk_buff刚创建时,结构如下
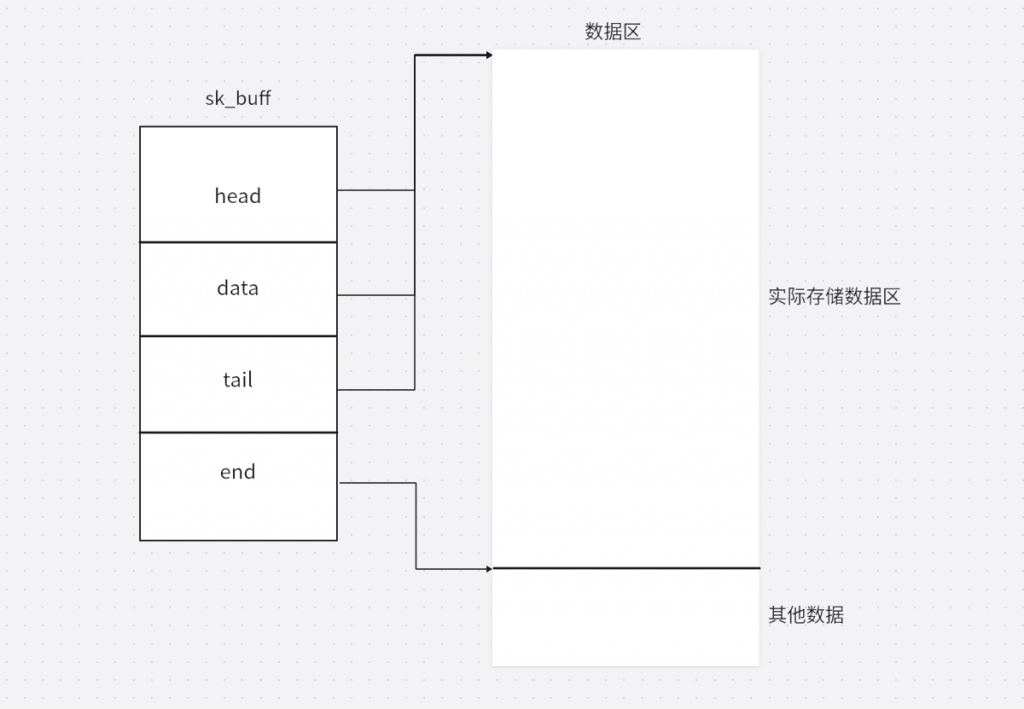
sk_buff初始化后,data和tail被放到实际存储数据的中间
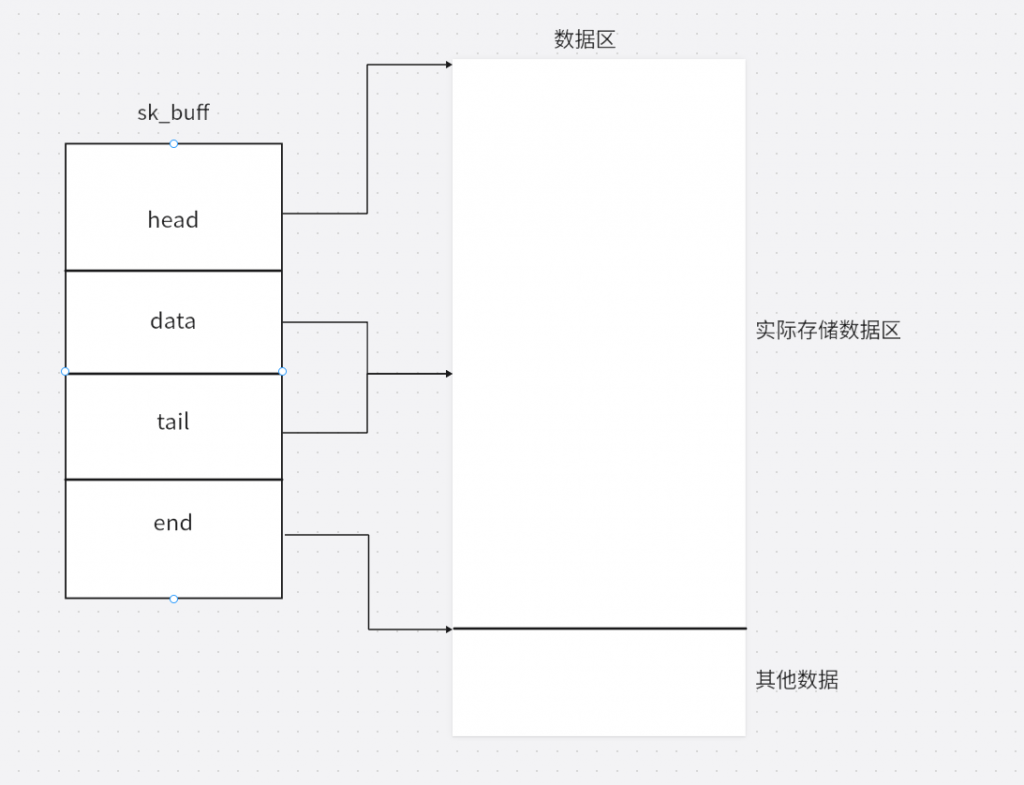
存放对应用数据时会调用skb_reserve函数是tail向下移动,得到一片区域存放应用数据,tail到end的这片数据被称为tailhome,data到head这篇区域被称为headhome。
static inline void skb_reserve(struct sk_buff *skb, int len)
{
skb->data += len;
skb->tail += len;
}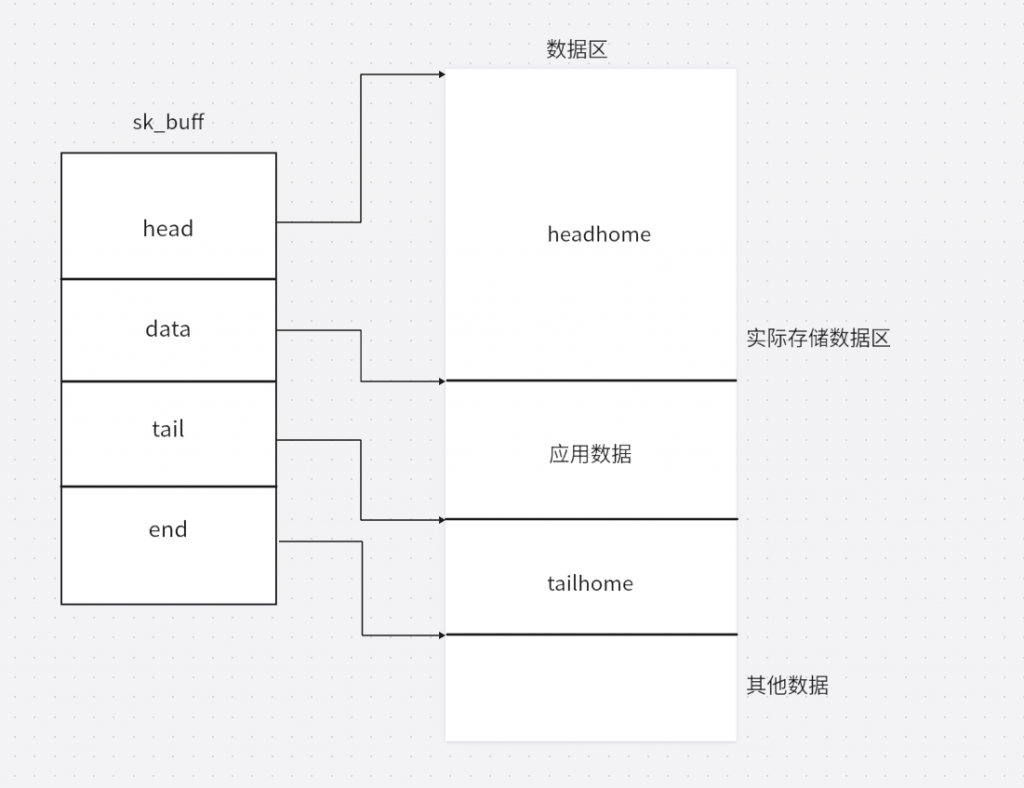
当各层想要往sk_buff添加协议数据时,会调用skb_push将data指针向上移动得到一片区域存放协议数据,通常向上扩展的长度是个层头部的大小。
在传输层中,tcp会在tcp_transmit_skb函数中调用skb_push向skb添加tcp头部信息,data上移的大小正好是tcp_header_size。
static int __tcp_transmit_skb(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb,
int clone_it, gfp_t gfp_mask, u32 rcv_nxt)
{
skb_push(skb, tcp_header_size);
skb_reset_transport_header(skb);
skb->sk = sk;
th = (struct tcphdr *)skb->data;
th->source = inet->inet_sport;
th->dest = inet->inet_dport;
th->seq = htonl(tcb->seq);
th->ack_seq = htonl(rcv_nxt);
*(((__be16 *)th) + 6) = htons(((tcp_header_size >> 2) << 12) |tcb->tcp_flags);
th->check = 0;
th->urg_ptr = 0;
.....................
}在skb_reset_transport_header函数中设置了sk_buff的transport_header存放着传输层协议数据在数据区的偏移。
static inline void skb_reset_transport_header(struct sk_buff *skb)
{
skb->transport_header = skb->data - skb->head;
}request_sock_queue
request_sock_queue即连接请求队列。
Socket
socket与sock
socket结构体是Linux网络协议栈最为重要的结构体。其结构体如下所示
struct socket {
socket_state state;
kmemcheck_bitfield_begin(type);
short type;
kmemcheck_bitfield_end(type);
unsigned long flags;
struct socket_wq __rcu *wq;
struct file *file;
struct sock *sk;
const struct proto_ops *ops;
};socket是提供给上层用户调用的结构体,我们调用socket函数返回的结构体为socket,其对应下层的结构体为sock,sock是给内核底层使用的,包括了很多信息,在socket结构体中记录着与之对应的sock结构体。
struct socket {
.......................
struct sock *sk;
.......................
};sock结构体如下
sock结构体
struct sock {
/*
* Now struct inet_timewait_sock also uses sock_common, so please just
* don't add nothing before this first member (__sk_common) --acme
*/
struct sock_common __sk_common;
#define sk_node __sk_common.skc_node
#define sk_nulls_node __sk_common.skc_nulls_node
#define sk_refcnt __sk_common.skc_refcnt
#define sk_tx_queue_mapping __sk_common.skc_tx_queue_mapping
#define sk_dontcopy_begin __sk_common.skc_dontcopy_begin
#define sk_dontcopy_end __sk_common.skc_dontcopy_end
#define sk_hash __sk_common.skc_hash
#define sk_portpair __sk_common.skc_portpair
#define sk_num __sk_common.skc_num
#define sk_dport __sk_common.skc_dport
#define sk_addrpair __sk_common.skc_addrpair
#define sk_daddr __sk_common.skc_daddr
#define sk_rcv_saddr __sk_common.skc_rcv_saddr
#define sk_family __sk_common.skc_family
#define sk_state __sk_common.skc_state
#define sk_reuse __sk_common.skc_reuse
#define sk_reuseport __sk_common.skc_reuseport
#define sk_ipv6only __sk_common.skc_ipv6only
#define sk_net_refcnt __sk_common.skc_net_refcnt
#define sk_bound_dev_if __sk_common.skc_bound_dev_if
#define sk_bind_node __sk_common.skc_bind_node
#define sk_prot __sk_common.skc_prot
#define sk_net __sk_common.skc_net
#define sk_v6_daddr __sk_common.skc_v6_daddr
#define sk_v6_rcv_saddr __sk_common.skc_v6_rcv_saddr
#define sk_cookie __sk_common.skc_cookie
#define sk_incoming_cpu __sk_common.skc_incoming_cpu
#define sk_flags __sk_common.skc_flags
#define sk_rxhash __sk_common.skc_rxhash
socket_lock_t sk_lock;
struct sk_buff_head sk_receive_queue;
/*
* The backlog queue is special, it is always used with
* the per-socket spinlock held and requires low latency
* access. Therefore we special case it's implementation.
* Note : rmem_alloc is in this structure to fill a hole
* on 64bit arches, not because its logically part of
* backlog.
*/
struct {
atomic_t rmem_alloc;
int len;
struct sk_buff *head;
struct sk_buff *tail;
} sk_backlog;
#define sk_rmem_alloc sk_backlog.rmem_alloc
int sk_forward_alloc;
__u32 sk_txhash;
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_RX_BUSY_POLL
unsigned int sk_napi_id;
unsigned int sk_ll_usec;
#endif
atomic_t sk_drops;
int sk_rcvbuf;
struct sk_filter __rcu *sk_filter;
union {
struct socket_wq __rcu *sk_wq;
struct socket_wq *sk_wq_raw;
};
#ifdef CONFIG_XFRM
struct xfrm_policy __rcu *sk_policy[2];
#endif
struct dst_entry __rcu *sk_rx_dst;
struct dst_entry __rcu *sk_dst_cache;
/* Note: 32bit hole on 64bit arches */
atomic_t sk_wmem_alloc;
atomic_t sk_omem_alloc;
int sk_sndbuf;
struct sk_buff_head sk_write_queue;
/*
* Because of non atomicity rules, all
* changes are protected by socket lock.
*/
kmemcheck_bitfield_begin(flags);
unsigned int sk_padding : 2,
sk_no_check_tx : 1,
sk_no_check_rx : 1,
sk_userlocks : 4,
sk_protocol : 8,
sk_type : 16;
#define SK_PROTOCOL_MAX U8_MAX
kmemcheck_bitfield_end(flags);
int sk_wmem_queued;
gfp_t sk_allocation;
u32 sk_pacing_rate; /* bytes per second */
u32 sk_max_pacing_rate;
netdev_features_t sk_route_caps;
netdev_features_t sk_route_nocaps;
int sk_gso_type;
unsigned int sk_gso_max_size;
u16 sk_gso_max_segs;
int sk_rcvlowat;
unsigned long sk_lingertime;
struct sk_buff_head sk_error_queue;
struct proto *sk_prot_creator;
rwlock_t sk_callback_lock;
int sk_err,
sk_err_soft;
u32 sk_ack_backlog;
u32 sk_max_ack_backlog;
__u32 sk_priority;
__u32 sk_mark;
spinlock_t sk_peer_lock;
struct pid *sk_peer_pid;
const struct cred *sk_peer_cred;
long sk_rcvtimeo;
long sk_sndtimeo;
struct timer_list sk_timer;
ktime_t sk_stamp;
#if BITS_PER_LONG==32
seqlock_t sk_stamp_seq;
#endif
u16 sk_tsflags;
u8 sk_shutdown;
u32 sk_tskey;
struct socket *sk_socket;
void *sk_user_data;
struct page_frag sk_frag;
struct sk_buff *sk_send_head;
__s32 sk_peek_off;
int sk_write_pending;
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
void *sk_security;
#endif
struct sock_cgroup_data sk_cgrp_data;
struct mem_cgroup *sk_memcg;
void (*sk_state_change)(struct sock *sk);
void (*sk_data_ready)(struct sock *sk);
void (*sk_write_space)(struct sock *sk);
void (*sk_error_report)(struct sock *sk);
int (*sk_backlog_rcv)(struct sock *sk,
struct sk_buff *skb);
void (*sk_destruct)(struct sock *sk);
struct sock_reuseport __rcu *sk_reuseport_cb;
struct rcu_head sk_rcu;
};socket结构体的创建
先看一下socket函数的原型
int socket(int domain, int type, int protocol);domain(协议族/地址族)
domain表示socket如何解释地址以及它可以通信的网络范围。
- AF_INET-----IPv4网络协议
- AF_INET6----IPv6网络协议
- AF_BLUETOOTH-----蓝牙通信
type(Socket类型)
type表示socket的通讯类型,传输方式等
- SOCK_STREAM-----面向连接的可靠字节流 TCP(ssh,http)
- SOCK_DGRAM -----无连接的消息传递 UDP(DNS)
protocol(具体协议)
protocol表示选择协议簇中的具体协议,为NULL表示使用该协议簇的默认协议
- IPPROTO_TCP----传输控制协议
- IPPROTO_UDP----用户数据报协议
在/net/socket.c中可以看见socket的系统调用。
Socket系统调用
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(socket, int, family, int, type, int, protocol)
{
int retval;
struct socket *sock;
int flags;
/* Check the SOCK_* constants for consistency. */
BUILD_BUG_ON(SOCK_CLOEXEC != O_CLOEXEC);
BUILD_BUG_ON((SOCK_MAX | SOCK_TYPE_MASK) != SOCK_TYPE_MASK);
BUILD_BUG_ON(SOCK_CLOEXEC & SOCK_TYPE_MASK);
BUILD_BUG_ON(SOCK_NONBLOCK & SOCK_TYPE_MASK);
flags = type & ~SOCK_TYPE_MASK;
if (flags & ~(SOCK_CLOEXEC | SOCK_NONBLOCK))
return -EINVAL;
type &= SOCK_TYPE_MASK;
if (SOCK_NONBLOCK != O_NONBLOCK && (flags & SOCK_NONBLOCK))
flags = (flags & ~SOCK_NONBLOCK) | O_NONBLOCK;
retval = sock_create(family, type, protocol, &sock);
if (retval < 0)
goto out;
retval = sock_map_fd(sock, flags & (O_CLOEXEC | O_NONBLOCK));
if (retval < 0)
goto out_release;
out:
/* It may be already another descriptor 8) Not kernel problem. */
return retval;
out_release:
sock_release(sock);
return retval;
}主要函数如下
- sock_create
- sock_map_fd
sock_create
sock_create原型如下
int sock_create(int family, int type, int proto, struct socket **res);sock_create->__sock_create
__sock_create
int __sock_create(struct net *net, int family, int type, int protocol,
struct socket **res, int kern)
{
int err;
struct socket *sock;
const struct net_proto_family *pf;
/*
* Check protocol is in range
*/
if (family < 0 || family >= NPROTO)
return -EAFNOSUPPORT;
if (type < 0 || type >= SOCK_MAX)
return -EINVAL;
/* Compatibility.
This uglymoron is moved from INET layer to here to avoid
deadlock in module load.
*/
if (family == PF_INET && type == SOCK_PACKET) {
pr_info_once("%s uses obsolete (PF_INET,SOCK_PACKET)\n",
current->comm);
family = PF_PACKET;
}
err = security_socket_create(family, type, protocol, kern);
if (err)
return err;
/*
* Allocate the socket and allow the family to set things up. if
* the protocol is 0, the family is instructed to select an appropriate
* default.
*/
sock = sock_alloc();
if (!sock) {
net_warn_ratelimited("socket: no more sockets\n");
return -ENFILE; /* Not exactly a match, but its the
closest posix thing */
}
sock->type = type;
#ifdef CONFIG_MODULES
/* Attempt to load a protocol module if the find failed.
*
* 12/09/1996 Marcin: But! this makes REALLY only sense, if the user
* requested real, full-featured networking support upon configuration.
* Otherwise module support will break!
*/
if (rcu_access_pointer(net_families[family]) == NULL)
request_module("net-pf-%d", family);
#endif
rcu_read_lock();
pf = rcu_dereference(net_families[family]);
err = -EAFNOSUPPORT;
if (!pf)
goto out_release;
/*
* We will call the ->create function, that possibly is in a loadable
* module, so we have to bump that loadable module refcnt first.
*/
if (!try_module_get(pf->owner))
goto out_release;
/* Now protected by module ref count */
rcu_read_unlock();
err = pf->create(net, sock, protocol, kern);
if (err < 0)
goto out_module_put;
/*
* Now to bump the refcnt of the [loadable] module that owns this
* socket at sock_release time we decrement its refcnt.
*/
if (!try_module_get(sock->ops->owner))
goto out_module_busy;
/*
* Now that we're done with the ->create function, the [loadable]
* module can have its refcnt decremented
*/
module_put(pf->owner);
err = security_socket_post_create(sock, family, type, protocol, kern);
if (err)
goto out_sock_release;
*res = sock;
return 0;
out_module_busy:
err = -EAFNOSUPPORT;
out_module_put:
sock->ops = NULL;
module_put(pf->owner);
out_sock_release:
sock_release(sock);
return err;
out_release:
rcu_read_unlock();
goto out_sock_release;
}简化后如以下所示
int __sock_create(struct net *net, int family, int type, int protocol,
struct socket **res, int kern)
{
sock =sock_alloc();
sock->type = type;
rcu_read_lock();
pf = rcu_dereference(net_families[family]);
err = pf->create(net, sock, protocol, kern);
}- 调用sock_alloc函数创建一个socket结构体
- 将socket结构体的type赋值为参数的type
- 将net_families[family]赋值给pf
- 调用pf的create函数
net_families在上述初始化中已经讲到了。这样我们的pf->create就执行了inet_family_ops ->create即inet_create,完整代码如下
inet_create
static int inet_create(struct net *net, struct socket *sock, int protocol,
int kern)
{
struct sock *sk;
struct inet_protosw *answer;
struct inet_sock *inet;
struct proto *answer_prot;
unsigned char answer_flags;
int try_loading_module = 0;
int err;
if (protocol < 0 || protocol >= IPPROTO_MAX)
return -EINVAL;
sock->state = SS_UNCONNECTED;
/* Look for the requested type/protocol pair. */
lookup_protocol:
err = -ESOCKTNOSUPPORT;
rcu_read_lock();
list_for_each_entry_rcu(answer, &inetsw[sock->type], list) {
err = 0;
/* Check the non-wild match. */
if (protocol == answer->protocol) {
if (protocol != IPPROTO_IP)
break;
} else {
/* Check for the two wild cases. */
if (IPPROTO_IP == protocol) {
protocol = answer->protocol;
break;
}
if (IPPROTO_IP == answer->protocol)
break;
}
err = -EPROTONOSUPPORT;
}
if (unlikely(err)) {
if (try_loading_module < 2) {
rcu_read_unlock();
/*
* Be more specific, e.g. net-pf-2-proto-132-type-1
* (net-pf-PF_INET-proto-IPPROTO_SCTP-type-SOCK_STREAM)
*/
if (++try_loading_module == 1)
request_module("net-pf-%d-proto-%d-type-%d",
PF_INET, protocol, sock->type);
/*
* Fall back to generic, e.g. net-pf-2-proto-132
* (net-pf-PF_INET-proto-IPPROTO_SCTP)
*/
else
request_module("net-pf-%d-proto-%d",
PF_INET, protocol);
goto lookup_protocol;
} else
goto out_rcu_unlock;
}
err = -EPERM;
if (sock->type == SOCK_RAW && !kern &&
!ns_capable(net->user_ns, CAP_NET_RAW))
goto out_rcu_unlock;
sock->ops = answer->ops;
answer_prot = answer->prot;
answer_flags = answer->flags;
rcu_read_unlock();
WARN_ON(!answer_prot->slab);
err = -ENOBUFS;
sk = sk_alloc(net, PF_INET, GFP_KERNEL, answer_prot, kern);
if (!sk)
goto out;
err = 0;
if (INET_PROTOSW_REUSE & answer_flags)
sk->sk_reuse = SK_CAN_REUSE;
inet = inet_sk(sk);
inet->is_icsk = (INET_PROTOSW_ICSK & answer_flags) != 0;
inet->nodefrag = 0;
if (SOCK_RAW == sock->type) {
inet->inet_num = protocol;
if (IPPROTO_RAW == protocol)
inet->hdrincl = 1;
}
if (net->ipv4.sysctl_ip_no_pmtu_disc)
inet->pmtudisc = IP_PMTUDISC_DONT;
else
inet->pmtudisc = IP_PMTUDISC_WANT;
inet->inet_id = 0;
sock_init_data(sock, sk);
sk->sk_destruct = inet_sock_destruct;
sk->sk_protocol = protocol;
sk->sk_backlog_rcv = sk->sk_prot->backlog_rcv;
inet->uc_ttl = -1;
inet->mc_loop = 1;
inet->mc_ttl = 1;
inet->mc_all = 1;
inet->mc_index = 0;
inet->mc_list = NULL;
inet->rcv_tos = 0;
sk_refcnt_debug_inc(sk);
if (inet->inet_num) {
/* It assumes that any protocol which allows
* the user to assign a number at socket
* creation time automatically
* shares.
*/
inet->inet_sport = htons(inet->inet_num);
/* Add to protocol hash chains. */
err = sk->sk_prot->hash(sk);
if (err) {
sk_common_release(sk);
goto out;
}
}
if (sk->sk_prot->init) {
err = sk->sk_prot->init(sk);
if (err)
sk_common_release(sk);
}
out:
return err;
out_rcu_unlock:
rcu_read_unlock();
goto out;
}inet_create简化后
static int inet_create(struct net *net, struct socket *sock, int protocol,
int kern)
{
struct sock *sk;
struct inet_protosw *answer;
struct proto *answer_prot;
list_for_each_entry_rcu(answer, &inetsw[sock->type], list) {
if (protocol == answer->protocol) {
if (protocol != IPPROTO_IP)
break;
}
sock->ops = answer->ops;
answer_prot = answer->prot;
answer_flags = answer->flags;
sk = sk_alloc(net, PF_INET, GFP_KERNEL, answer_prot, kern);
if (sk->sk_prot->init) {
err = sk->sk_prot->init(sk);
if (err)
sk_common_release(sk);
}
}list_for_each_entry_rcu用于遍历inetsw数组并将数组的元素给到answer,并判断socket函数传进来的protocol 是否等于answer->protocol。tcp的inet_protosw结构体如下。
{
.type = SOCK_STREAM,
.protocol = IPPROTO_TCP,
.prot = &tcp_prot,
.ops = &inet_stream_ops,
.flags = INET_PROTOSW_PERMANENT |
INET_PROTOSW_ICSK,
}sock->ops = answer->ops=inet_stream_ops
answer_prot=tcp_prot
answer_flags =INET_PROTOSW_PERMANENT |INET_PROTOSW_ICSK
tcp_prot
struct proto tcp_prot = {
.name = "TCP",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.close = tcp_close,
.connect = tcp_v4_connect,
.disconnect = tcp_disconnect,
.accept = inet_csk_accept,
.ioctl = tcp_ioctl,
.init = tcp_v4_init_sock,
.destroy = tcp_v4_destroy_sock,
.shutdown = tcp_shutdown,
.setsockopt = tcp_setsockopt,
.getsockopt = tcp_getsockopt,
.recvmsg = tcp_recvmsg,
.sendmsg = tcp_sendmsg,
.sendpage = tcp_sendpage,
.backlog_rcv = tcp_v4_do_rcv,
.release_cb = tcp_release_cb,
.hash = inet_hash,
.unhash = inet_unhash,
.get_port = inet_csk_get_port,
.enter_memory_pressure = tcp_enter_memory_pressure,
.stream_memory_free = tcp_stream_memory_free,
.sockets_allocated = &tcp_sockets_allocated,
.orphan_count = &tcp_orphan_count,
.memory_allocated = &tcp_memory_allocated,
.memory_pressure = &tcp_memory_pressure,
.sysctl_mem = sysctl_tcp_mem,
.sysctl_wmem = sysctl_tcp_wmem,
.sysctl_rmem = sysctl_tcp_rmem,
.max_header = MAX_TCP_HEADER,
.obj_size = sizeof(struct tcp_sock),
.slab_flags = SLAB_DESTROY_BY_RCU,
.twsk_prot = &tcp_timewait_sock_ops,
.rsk_prot = &tcp_request_sock_ops,
.h.hashinfo = &tcp_hashinfo,
.no_autobind = true,
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
.compat_setsockopt = compat_tcp_setsockopt,
.compat_getsockopt = compat_tcp_getsockopt,
#endif
.diag_destroy = tcp_abort,
};sk_alloc创建了一个sock结构体,详见初始化的sock模块
在后续的inet_create中判断了sk->sk_prot->init即tcp_prot->init是否存在,若存在则执行,不存在则不执行。
sock_map_fd
sock_create执行结束后我们得到了一个socket结构体和一个sock结构体,在socket系统调用时,我们传进去了一个socket结构体的引用。
retval = sock_create(family, type, protocol, &sock);在inet_create结尾将这个引用解引用并赋值为我们创建的socket结构体。
*res = sock;sock_map_fd函数如下,其作用是将socket结构体与文件描述符进行绑定,就像0表示标准输入,1表示标准输出,2表示标准错误输出,在没打开其他文件的情况下,我们新创建的socket结构体的文件描述符为3。
retval = sock_map_fd(sock, flags & (O_CLOEXEC | O_NONBLOCK));
static int sock_map_fd(struct socket *sock, int flags)
{
struct file *newfile;
int fd = get_unused_fd_flags(flags);
newfile = sock_alloc_file(sock, flags, NULL);
if (likely(!IS_ERR(newfile))) {
fd_install(fd, newfile);
return fd;
}
return PTR_ERR(newfile);
}Bind
bind函数原型,
int bind(int sockfd, const struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t addrlen);- sockfd:socket对应的文件描述符
- addr:一个sockaddr结构体,里面包含协议簇和端口
- addrlen:addr的长度
在Socket.c中可以找到对应的系统调用
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(bind, int, fd, struct sockaddr __user *, umyaddr, int, addrlen)
{
struct socket *sock;
struct sockaddr_storage address;
int err, fput_needed;
sock = sockfd_lookup_light(fd, &err, &fput_needed);
if (sock) {
err = move_addr_to_kernel(umyaddr, addrlen, &address);
if (err >= 0) {
err = security_socket_bind(sock,(struct sockaddr *)&address,addrlen);
if (!err)
err = sock->ops->bind(sock,(struct sockaddr *&address, addrlen);
}
}
return err;
}- 通过sockfd_lookup_light用传进来的文件描述符fd找到对应的socket结构体。
- move_addr_to_kernel用copy_form_user从用户态把sockaddr结构体赋值到内核态空间的sockaddr_storage结构体中。
- 调用sock->ops->bind
inet_bind
在sock_create函数中我们知道了sock->ops=anser->ops=inet_stream_ops,inet_stream_ops结构体如下
inet_stream_ops
const struct proto_ops inet_stream_ops = {
.family = PF_INET,
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.release = inet_release,
.bind = inet_bind,
.connect = inet_stream_connect,
.socketpair = sock_no_socketpair,
.accept = inet_accept,
.getname = inet_getname,
.poll = tcp_poll,
.ioctl = inet_ioctl,
.gettstamp = sock_gettstamp,
.listen = inet_listen,
.shutdown = inet_shutdown,
.setsockopt = sock_common_setsockopt,
.getsockopt = sock_common_getsockopt,
.sendmsg = inet_sendmsg,
.recvmsg = inet_recvmsg,
#ifdef CONFIG_MMU
.mmap = tcp_mmap,
#endif
.splice_eof = inet_splice_eof,
.splice_read = tcp_splice_read,
.set_peek_off = sk_set_peek_off,
.read_sock = tcp_read_sock,
.read_skb = tcp_read_skb,
.sendmsg_locked = tcp_sendmsg_locked,
.peek_len = tcp_peek_len,
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
.compat_ioctl = inet_compat_ioctl,
#endif
.set_rcvlowat = tcp_set_rcvlowat,
};所以sock->ops->bind=inet_bind
inet_bind又调用了inet_bind_sk
int inet_bind(struct socket *sock, struct sockaddr *uaddr, int addr_len)
{
return inet_bind_sk(sock->sk, uaddr, addr_len);
}inet_bind_sk。这里就有点多态的影子了,判断是否重写了bind方法,如果重写了就执行sk->sk_prot->bind,没重写就执行父类的bind方法。
int inet_bind_sk(struct sock *sk, struct sockaddr *uaddr, int addr_len)
{
if (sk->sk_prot->bind) {
return sk->sk_prot->bind(sk, uaddr, addr_len);
return __inet_bind(sk, uaddr, addr_len, flags);
}在tcp_prot中并没有重写bind方法,执行__inet_bind
__inet_bind函数
int __inet_bind(struct sock *sk, struct sockaddr *uaddr, int addr_len,
u32 flags)
{
struct sockaddr_in *addr = (struct sockaddr_in *)uaddr;
struct inet_sock *inet = inet_sk(sk);
struct net *net = sock_net(sk);
unsigned short snum;
int chk_addr_ret;
u32 tb_id = RT_TABLE_LOCAL;
int err;
if (addr->sin_family != AF_INET) {
/* Compatibility games : accept AF_UNSPEC (mapped to AF_INET)
* only if s_addr is INADDR_ANY.
*/
err = -EAFNOSUPPORT;
if (addr->sin_family != AF_UNSPEC ||
addr->sin_addr.s_addr != htonl(INADDR_ANY))
goto out;
}
tb_id = l3mdev_fib_table_by_index(net, sk->sk_bound_dev_if) ? : tb_id;
chk_addr_ret = inet_addr_type_table(net, addr->sin_addr.s_addr, tb_id);
/* Not specified by any standard per-se, however it breaks too
* many applications when removed. It is unfortunate since
* allowing applications to make a non-local bind solves
* several problems with systems using dynamic addressing.
* (ie. your servers still start up even if your ISDN link
* is temporarily down)
*/
err = -EADDRNOTAVAIL;
if (!inet_addr_valid_or_nonlocal(net, inet, addr->sin_addr.s_addr,
chk_addr_ret))
goto out;
snum = ntohs(addr->sin_port);
err = -EACCES;
if (!(flags & BIND_NO_CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE) &&
snum && inet_port_requires_bind_service(net, snum) &&
!ns_capable(net->user_ns, CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE))
goto out;
/* We keep a pair of addresses. rcv_saddr is the one
* used by hash lookups, and saddr is used for transmit.
*
* In the BSD API these are the same except where it
* would be illegal to use them (multicast/broadcast) in
* which case the sending device address is used.
*/
if (flags & BIND_WITH_LOCK)
lock_sock(sk);
/* Check these errors (active socket, double bind). */
err = -EINVAL;
if (sk->sk_state != TCP_CLOSE || inet->inet_num)
goto out_release_sock;
inet->inet_rcv_saddr = inet->inet_saddr = addr->sin_addr.s_addr;
if (chk_addr_ret == RTN_MULTICAST || chk_addr_ret == RTN_BROADCAST)
inet->inet_saddr = 0; /* Use device */
/* Make sure we are allowed to bind here. */
if (snum || !(inet_test_bit(BIND_ADDRESS_NO_PORT, sk) ||
(flags & BIND_FORCE_ADDRESS_NO_PORT))) {
err = sk->sk_prot->get_port(sk, snum);
if (err) {
inet->inet_saddr = inet->inet_rcv_saddr = 0;
goto out_release_sock;
}
if (!(flags & BIND_FROM_BPF)) {
err = BPF_CGROUP_RUN_PROG_INET4_POST_BIND(sk);
if (err) {
inet->inet_saddr = inet->inet_rcv_saddr = 0;
if (sk->sk_prot->put_port)
sk->sk_prot->put_port(sk);
goto out_release_sock;
}
}
}
if (inet->inet_rcv_saddr)
sk->sk_userlocks |= SOCK_BINDADDR_LOCK;
if (snum)
sk->sk_userlocks |= SOCK_BINDPORT_LOCK;
inet->inet_sport = htons(inet->inet_num);
inet->inet_daddr = 0;
inet->inet_dport = 0;
sk_dst_reset(sk);
err = 0;
out_release_sock:
if (flags & BIND_WITH_LOCK)
release_sock(sk);
out:
return err;
}简化后如下
int __inet_bind(struct sock *sk, struct sockaddr *uaddr, int addr_len,
u32 flags)
{
struct sockaddr_in *addr = (struct sockaddr_in *)uaddr;
struct inet_sock *inet = inet_sk(sk);
struct net *net = sock_net(sk);
unsigned short snum;
int chk_addr_ret;
u32 tb_id = RT_TABLE_LOCAL;
int err;
snum = ntohs(addr->sin_port);
if (sk->sk_state != TCP_CLOSE || inet->inet_num)
goto out_release_sock;
inet->inet_rcv_saddr = inet->inet_saddr = addr->sin_addr.s_addr;
if (snum || !(inet_test_bit(BIND_ADDRESS_NO_PORT, sk) ||
(flags & BIND_FORCE_ADDRESS_NO_PORT))) {
err = sk->sk_prot->get_port(sk, snum);
if (err) {
inet->inet_saddr = inet->inet_rcv_saddr = 0;
if (sk->sk_prot->put_port)
sk->sk_prot->put_port(sk);
goto out_release_sock;
return err;
}- snum=我们设定的端口
- inet->inet_rcv_saddr=inet->inet_saddr=设定的地址,sock到inet_sock的转化具体见sock的初始化
- 如果我们指定了端口则进入sk->sk_prot->get_port(sk, snum);中
- 执行sk->sk_prot->get_port发生错误则执行sk->sk_prot->put_port
inet_csk_get_port
sk->sk_prot->get_port即tcp_prot->get_port=inet_csk_get_port。该部分比较长,源码如下
inet_csk_get_port
int inet_csk_get_port(struct sock *sk, unsigned short snum)
{
bool reuse = sk->sk_reuse && sk->sk_state != TCP_LISTEN;
struct inet_hashinfo *hinfo = sk->sk_prot->h.hashinfo;
int ret = 1, attempts = 5, port = snum;
int smallest_size = -1, smallest_port;
struct inet_bind_hashbucket *head;
struct net *net = sock_net(sk);
int i, low, high, attempt_half;
struct inet_bind_bucket *tb;
kuid_t uid = sock_i_uid(sk);
u32 remaining, offset;
if (port) {
have_port:
head = &hinfo->bhash[inet_bhashfn(net, port,
hinfo->bhash_size)];
spin_lock_bh(&head->lock);
inet_bind_bucket_for_each(tb, &head->chain)
if (net_eq(ib_net(tb), net) && tb->port == port)
goto tb_found;
goto tb_not_found;
}
again:
attempt_half = (sk->sk_reuse == SK_CAN_REUSE) ? 1 : 0;
other_half_scan:
inet_get_local_port_range(net, &low, &high);
high++; /* [32768, 60999] -> [32768, 61000[ */
if (high - low < 4)
attempt_half = 0;
if (attempt_half) {
int half = low + (((high - low) >> 2) << 1);
if (attempt_half == 1)
high = half;
else
low = half;
}
remaining = high - low;
if (likely(remaining > 1))
remaining &= ~1U;
offset = prandom_u32() % remaining;
/* __inet_hash_connect() favors ports having @low parity
* We do the opposite to not pollute connect() users.
*/
offset |= 1U;
smallest_size = -1;
smallest_port = low; /* avoid compiler warning */
other_parity_scan:
port = low + offset;
for (i = 0; i < remaining; i += 2, port += 2) {
if (unlikely(port >= high))
port -= remaining;
if (inet_is_local_reserved_port(net, port))
continue;
head = &hinfo->bhash[inet_bhashfn(net, port,
hinfo->bhash_size)];
spin_lock_bh(&head->lock);
inet_bind_bucket_for_each(tb, &head->chain)
if (net_eq(ib_net(tb), net) && tb->port == port) {
if (((tb->fastreuse > 0 && reuse) ||
(tb->fastreuseport > 0 &&
sk->sk_reuseport &&
!rcu_access_pointer(sk->sk_reuseport_cb) &&
uid_eq(tb->fastuid, uid))) &&
(tb->num_owners < smallest_size || smallest_size == -1)) {
smallest_size = tb->num_owners;
smallest_port = port;
}
if (!inet_csk(sk)->icsk_af_ops->bind_conflict(sk, tb, false))
goto tb_found;
goto next_port;
}
goto tb_not_found;
next_port:
spin_unlock_bh(&head->lock);
cond_resched();
}
if (smallest_size != -1) {
port = smallest_port;
goto have_port;
}
offset--;
if (!(offset & 1))
goto other_parity_scan;
if (attempt_half == 1) {
/* OK we now try the upper half of the range */
attempt_half = 2;
goto other_half_scan;
}
return ret;
tb_not_found:
tb = inet_bind_bucket_create(hinfo->bind_bucket_cachep,
net, head, port);
if (!tb)
goto fail_unlock;
tb_found:
if (!hlist_empty(&tb->owners)) {
if (sk->sk_reuse == SK_FORCE_REUSE)
goto success;
if (((tb->fastreuse > 0 && reuse) ||
(tb->fastreuseport > 0 &&
!rcu_access_pointer(sk->sk_reuseport_cb) &&
sk->sk_reuseport && uid_eq(tb->fastuid, uid))) &&
smallest_size == -1)
goto success;
if (inet_csk(sk)->icsk_af_ops->bind_conflict(sk, tb, true)) {
if ((reuse ||
(tb->fastreuseport > 0 &&
sk->sk_reuseport &&
!rcu_access_pointer(sk->sk_reuseport_cb) &&
uid_eq(tb->fastuid, uid))) &&
smallest_size != -1 && --attempts >= 0) {
spin_unlock_bh(&head->lock);
goto again;
}
goto fail_unlock;
}
}
inet_csk_update_fastreuse(tb, sk);
success:
if (!inet_csk(sk)->icsk_bind_hash)
inet_bind_hash(sk, tb, port);
WARN_ON(inet_csk(sk)->icsk_bind_hash != tb);
ret = 0;
fail_unlock:
spin_unlock_bh(&head->lock);
return ret;
}好像都挺重要的没啥可以删掉的。。
if (port) {
have_port:
head = &hinfo->bhash[inet_bhashfn(net, port,hinfo->bhash_size)];
spin_lock_bh(&head->lock);
inet_bind_bucket_for_each(tb, &head->chain)
if (net_eq(ib_net(tb), net) && tb->port == port)
goto tb_found;
goto tb_not_found;
}- 判断是否指定了端口
- 如果指定了端口则将端口作hash处理,并找到对应hash桶的inet_bind_hashbucket结构体
- 从对应的inet_bind_hashbucket结构体遍历inet_bind_bucket,具体详见必要知识
- 并对比找到的inet_bind_bucket结构体的端口是否等于传进来的端口
- 若找到对应的inet_bind_bucket结构体,则跳转到tb_found,未找到则跳转到tb_not_found
若未指定端口则执行以下函数
inet_get_local_port_range(net, &low, &high);
high++;
if (high - low < 4)
attempt_half = 0;
remaining = high - low;
if (likely(remaining > 1))
remaining &= ~1U;
offset = prandom_u32() % remaining;- 取到本地最小端口和最大端口,一般设置为(32768, 60999)
- 计算剩余空闲端口(remaining )
- 用随机数生成随机端口offset
接着进行端口的检查,以下代码经过简化,排除了端口复用的情况
other_half_scan:
port = low + offset;
for (i = 0; i < remaining; i += 2, port += 2) {
head = &hinfo->bhash[inet_bhashfn(net, port,hinfo->bhash_size)];
inet_bind_bucket_for_each(tb, &head->chain)
if (net_eq(ib_net(tb), net) && tb->port == port) {
if (!inet_csk(sk)->icsk_af_ops->bind_conflict(sk, tb, false))
goto tb_found;
goto next_port;
}
goto tb_not_found;
next_port:
offset--;
goto other_half_scan;
} - 用随机得到的端口进行hash计算并取得对应的inet_bind_hashbucket结构体
- 遍历inet_bind_hashbucket结构体找到所有inet_bind_bucket结构体对比端口号
- 若找到则判断该端口是否被占用,若没被占用则跳转至tb_found,若被占用则跳转到next_port
- 若没找到对应inet_bind_bucket结构体则跳转至tb_not_found
- next_port则将offset-1后进入下一次循环
将对应的inet_bind_bucket加入bhash中
tb_not_found:
tb = inet_bind_bucket_create(hinfo->bind_bucket_cachep,net, head, port);
tb_found:
if (!hlist_empty(&tb->owners)) {
if (sk->sk_reuse == SK_FORCE_REUSE)
goto success;
}
success:
if (!inet_csk(sk)->icsk_bind_hash)
inet_bind_hash(sk, tb, port);
ret = 0;- 若没找到对应的inet_bind_bucket结构体则创建一个并初始化(inet_bind_bucket_create)
- 若找到了inet_bind_bucket结构体,则判断inet_bind_bucket结构体对应的sock结构体是否允许复用
- 若允许或者inet_bind_bucket结构体对应的sock结构体为空则将inet_bind_bucket与sock结构体进行绑定
inet_bind_hash
void inet_bind_hash(struct sock *sk, struct inet_bind_bucket *tb,const unsigned short snum)
{
inet_sk(sk)->inet_num = snum;
sk_add_bind_node(sk, &tb->owners);
tb->num_owners++;
inet_csk(sk)->icsk_bind_hash = tb;
}- 将sock转换成inet_sk并将指定的端口保存在inet_num成员中
- 将inet_bind_bucket结构体的owners成员指向sock结构体,并将num_owners++
- 将sock转换成inet_connection_sock结构体并将inet_bind_bucket保存在icsk_bind_hash成员中
至此bind函数结束
总结
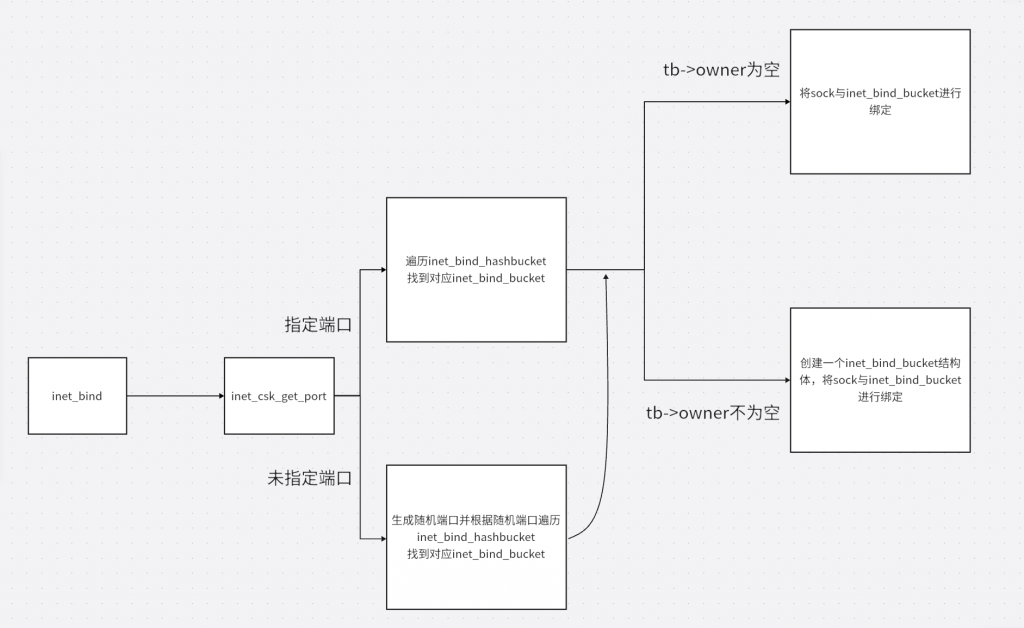
listen
listen函数原型如下
int listen(int sockfd, int backlog);- sockfd:想要监听socket的文件描述符
- backlog:进入队列中等待被处理的连接的最大数量,当有新的客户端连接请求时,如果已经有 backlog 个连接处于等待状态,新的连接请求将被拒绝
listen系统调用如下
SYSCALL_DEFINE2(listen, int, fd, int, backlog)
{
struct socket *sock;
int err, fput_needed;
int somaxconn;
sock = sockfd_lookup_light(fd, &err, &fput_needed);
if (sock) {
somaxconn = READ_ONCE(sock_net(sock->sk)->core.sysctl_somaxconn);
if ((unsigned int)backlog > somaxconn)
backlog = somaxconn;
err = security_socket_listen(sock, backlog);
if (!err)
err = sock->ops->listen(sock, backlog);
fput_light(sock->file, fput_needed);
}
return err;
}- sockfd_lookup_light根据对应fd找到socket结构体
- 执行sock->ops->listen即inet_stream_ops->listen=inet_listen
inet_listen
inet_listen函数如下
int inet_listen(struct socket *sock, int backlog)
{
struct sock *sk = sock->sk;
unsigned char old_state;
int err;
if (sock->state != SS_UNCONNECTED || sock->type != SOCK_STREAM)
goto out;
old_state = sk->sk_state;
if (!((1 << old_state) & (TCPF_CLOSE | TCPF_LISTEN)))
goto out;
if (old_state != TCP_LISTEN) {
err = inet_csk_listen_start(sk, backlog);
if (err)
goto out;
}
sk->sk_max_ack_backlog = backlog;
err = 0;
return err;
}- 判断当前socket的状态,如果当前socket处于SS_UNCONNECTED状态且类型是SOCK_STREAM就往下执行。
- 判断sock的状态,如果当前sock处于TCPF_CLOSE | TCPF_LISTEN 状态就往下继续执行,否则都终止。
- 执行inet_csk_listen_start
- 更新sk->sk_max_ack_backlog = backlog;
inet_csk_listen_start
inet_csk_listen_start如下
int inet_csk_listen_start(struct sock *sk, int backlog)
{
struct inet_connection_sock *icsk = inet_csk(sk);
struct inet_sock *inet = inet_sk(sk);
reqsk_queue_alloc(&icsk->icsk_accept_queue);
sk->sk_max_ack_backlog = backlog;
sk->sk_ack_backlog = 0;
inet_csk_delack_init(sk);
sk_state_store(sk, TCP_LISTEN);
if (!sk->sk_prot->get_port(sk, inet->inet_num)) {
inet->inet_sport = htons(inet->inet_num);
sk_dst_reset(sk);
err = sk->sk_prot->hash(sk);
if (likely(!err))
return 0;
sk->sk_state = TCP_CLOSE;
return err;
}- 用参数初始化sk_max_ack_backlog
- 将当前sock的状态设置为TCP_LISTEN
- 因为bind() 与 listen() 之间可能存在时间差,其他进程可能已占用该端口。所以需要重新调用sk->sk_prot->get_port检查端口是否冲突。
- 调用sk->sk_prot->hash将sock加入listening_hash
inet_hash
sk->sk_prot->hash=inet_hash,如下
int __inet_hash(struct sock *sk, struct sock *osk,
int (*saddr_same)(const struct sock *sk1,
const struct sock *sk2,
bool match_wildcard))
{
struct inet_hashinfo *hashinfo = sk->sk_prot->h.hashinfo;
struct inet_listen_hashbucket *ilb;
int err = 0;
if (sk->sk_state != TCP_LISTEN) {
inet_ehash_nolisten(sk, osk);
return 0;
}
ilb = &hashinfo->listening_hash[inet_sk_listen_hashfn(sk)];
spin_lock(&ilb->lock);
if (sk->sk_reuseport) {
err = inet_reuseport_add_sock(sk, ilb, saddr_same);
if (err)
goto unlock;
}
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_IPV6) && sk->sk_reuseport &&
sk->sk_family == AF_INET6)
__sk_nulls_add_node_tail_rcu(sk, &ilb->nulls_head);
else
__sk_nulls_add_node_rcu(sk, &ilb->nulls_head);
sock_set_flag(sk, SOCK_RCU_FREE);
sock_prot_inuse_add(sock_net(sk), sk->sk_prot, 1);
unlock:
spin_unlock(&ilb->lock);
return err;
}- 判断当前sock是否listing状态,若不是则退出
- 对端口号进行hash找到对应的inet_listening_bucket
- 判断当前协议簇调用不同函数将当前sock加入listening_hash
看一下__sk_nulls_add_node_rcu--->hlist_nulls_add_head_rcu
static inline void __sk_nulls_add_node_rcu(struct sock *sk, struct hlist_nulls_head *list)
{
hlist_nulls_add_head_rcu(&sk->sk_nulls_node, list);
}
hlist_nulls_add_head_rcu(struct hlist_nulls_node *n,struct hlist_nulls_head *h)
{
struct hlist_nulls_node *first = h->first;
n->next = first;
WRITE_ONCE(n->pprev, &h->first);
rcu_assign_pointer(hlist_nulls_first_rcu(h), n);
if (!is_a_nulls(first))
WRITE_ONCE(first->pprev, &n->next);
}- sk->sk_nulls_node->next=inet_listen_hashbucket->nulls_head->first
总结
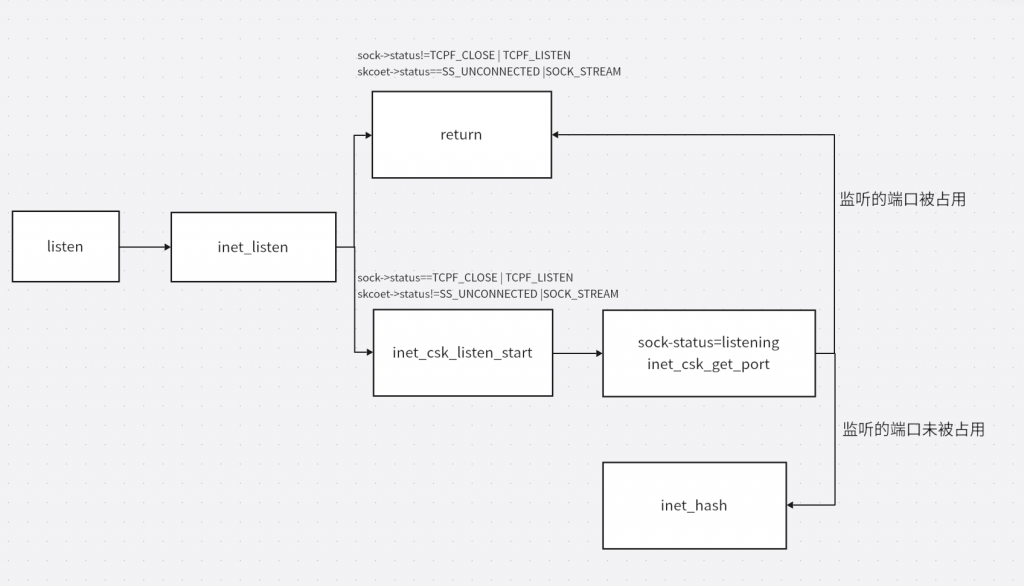
Connect
connect函数原型如下
int connect(int sockfd, const struct sockaddr *addr ,socklen_t addrlen);- sockfd:socket的文件描述符
- addr :连接的地址和端口以及协议簇
- addrlen:addr的长度
系统调用如下
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(connect, int, fd, struct sockaddr __user *, uservaddr,int, addrlen)
{
struct socket *sock;
struct sockaddr_storage address;
int err, fput_needed;
sock = sockfd_lookup_light(fd, &err, &fput_needed);
err = move_addr_to_kernel(uservaddr, addrlen, &address);
err = sock->ops->connect(sock, (struct sockaddr *)&address, addrlen,sock->file->f_flags);
return err;
}- 调用sockfd_lookup_light寻找与fd相关的socket
- 将addr移动到内核
- 调用inet_stream_ops->connect=inet_stream_connect
inet_stream_connect
简化代码如下,不考虑报错以及已连接状态
int __inet_stream_connect(struct socket *sock, struct sockaddr *uaddr,
int addr_len, int flags)
{
struct sock *sk = sock->sk;
int err;
long timeo;
switch (sock->state) {
case SS_UNCONNECTED:
if (sk->sk_state != TCP_CLOSE)
goto out;
err = sk->sk_prot->connect(sk, uaddr, addr_len);
sock->state = SS_CONNECTING;
break;
}
timeo = sock_sndtimeo(sk, flags & O_NONBLOCK);
if ((1 << sk->sk_state) & (TCPF_SYN_SENT | TCPF_SYN_RECV)) {
if (!timeo || !inet_wait_for_connect(sk, timeo, writebias))
goto out;
}
sock->state = SS_CONNECTED;
err = 0;
}- 根据sock->state选择执行的代码
- 在SS_UNCONNECTED状态下,若sock的状态不是TCP_CLOSE,则调用sk->sk_prot->connect
- 调用sock_sndtimeo判断该sock是否是阻塞的,若非阻塞则返回0,阻塞则返回对应等待的秒数
- 判断若sock是非阻塞的,则退出,若为阻塞则执行inet_wait_for_connect
tcp_v4_connect
源代码如下
tcp_v4_connect
int tcp_v4_connect(struct sock *sk, struct sockaddr *uaddr, int addr_len)
{
struct sockaddr_in *usin = (struct sockaddr_in *)uaddr;
struct inet_sock *inet = inet_sk(sk);
struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk);
__be16 orig_sport, orig_dport;
__be32 daddr, nexthop;
struct flowi4 *fl4;
struct rtable *rt;
int err;
struct ip_options_rcu *inet_opt;
if (addr_len < sizeof(struct sockaddr_in))
return -EINVAL;
if (usin->sin_family != AF_INET)
return -EAFNOSUPPORT;
nexthop = daddr = usin->sin_addr.s_addr;
inet_opt = rcu_dereference_protected(inet->inet_opt,
lockdep_sock_is_held(sk));
if (inet_opt && inet_opt->opt.srr) {
if (!daddr)
return -EINVAL;
nexthop = inet_opt->opt.faddr;
}
orig_sport = inet->inet_sport;
orig_dport = usin->sin_port;
fl4 = &inet->cork.fl.u.ip4;
rt = ip_route_connect(fl4, nexthop, inet->inet_saddr,
RT_CONN_FLAGS(sk), sk->sk_bound_dev_if,
IPPROTO_TCP,
orig_sport, orig_dport, sk);
if (IS_ERR(rt)) {
err = PTR_ERR(rt);
if (err == -ENETUNREACH)
IP_INC_STATS(sock_net(sk), IPSTATS_MIB_OUTNOROUTES);
return err;
}
if (rt->rt_flags & (RTCF_MULTICAST | RTCF_BROADCAST)) {
ip_rt_put(rt);
return -ENETUNREACH;
}
if (!inet_opt || !inet_opt->opt.srr)
daddr = fl4->daddr;
if (!inet->inet_saddr)
inet->inet_saddr = fl4->saddr;
sk_rcv_saddr_set(sk, inet->inet_saddr);
if (tp->rx_opt.ts_recent_stamp && inet->inet_daddr != daddr) {
/* Reset inherited state */
tp->rx_opt.ts_recent = 0;
tp->rx_opt.ts_recent_stamp = 0;
if (likely(!tp->repair))
tp->write_seq = 0;
}
if (tcp_death_row.sysctl_tw_recycle &&
!tp->rx_opt.ts_recent_stamp && fl4->daddr == daddr)
tcp_fetch_timewait_stamp(sk, &rt->dst);
inet->inet_dport = usin->sin_port;
sk_daddr_set(sk, daddr);
inet_csk(sk)->icsk_ext_hdr_len = 0;
if (inet_opt)
inet_csk(sk)->icsk_ext_hdr_len = inet_opt->opt.optlen;
tp->rx_opt.mss_clamp = TCP_MSS_DEFAULT;
/* Socket identity is still unknown (sport may be zero).
* However we set state to SYN-SENT and not releasing socket
* lock select source port, enter ourselves into the hash tables and
* complete initialization after this.
*/
tcp_set_state(sk, TCP_SYN_SENT);
err = inet_hash_connect(&tcp_death_row, sk);
if (err)
goto failure;
sk_set_txhash(sk);
rt = ip_route_newports(fl4, rt, orig_sport, orig_dport,
inet->inet_sport, inet->inet_dport, sk);
if (IS_ERR(rt)) {
err = PTR_ERR(rt);
rt = NULL;
goto failure;
}
/* OK, now commit destination to socket. */
sk->sk_gso_type = SKB_GSO_TCPV4;
sk_setup_caps(sk, &rt->dst);
if (!tp->write_seq && likely(!tp->repair))
tp->write_seq = secure_tcp_sequence_number(inet->inet_saddr,
inet->inet_daddr,
inet->inet_sport,
usin->sin_port);
inet->inet_id = prandom_u32();
err = tcp_connect(sk);
rt = NULL;
if (err)
goto failure;
return 0;
failure:
/*
* This unhashes the socket and releases the local port,
* if necessary.
*/
tcp_set_state(sk, TCP_CLOSE);
ip_rt_put(rt);
sk->sk_route_caps = 0;
inet->inet_dport = 0;
return err;
}简化后
int tcp_v4_connect(struct sock *sk, struct sockaddr *uaddr, int addr_len)
{
struct sockaddr_in *usin = (struct sockaddr_in *)uaddr;
struct inet_sock *inet = inet_sk(sk);
struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk);
__be16 orig_sport, orig_dport;
__be32 daddr, nexthop;
struct rtable *rt;
nexthop = daddr = usin->sin_addr.s_addr;
orig_sport = inet->inet_sport;
orig_dport = usin->sin_port;
rt = ip_route_connect(fl4, nexthop, inet->inet_saddr,RT_CONN_FLAGS(sk), sk->sk_bound_dev_if,IPPROTO_TCP,orig_sport, orig_dport, sk);
inet->inet_dport = usin->sin_port
sk_daddr_set(sk, daddr);
tcp_set_state(sk, TCP_SYN_SENT);
err = inet_hash_connect(&tcp_death_row, sk);
err = tcp_connect(sk);
return 0;
}- 从参数中获取目的IP,目的端口赋值给netxhop,orig_dport。在inet_bind_hash函数中我们将绑定的端口赋值给了inet_sk(sk)->inet_num,将该值赋值给orig_sport。
- 调用ip_route_connect根据目的IP进行路由规划
- 将目的端口赋值给inet->inet_dport,并设置该sock的状态为TCP_SYN_SENT
- 执行inet_hash_connect
- 执行tcp_connect
inet_hash_connect
代码如下
inet_hash_connect
int __inet_hash_connect(struct inet_timewait_death_row *death_row,
struct sock *sk, u64 port_offset,
int (*check_established)(struct inet_timewait_death_row *,
struct sock *, __u16, struct inet_timewait_sock **))
{
struct inet_hashinfo *hinfo = death_row->hashinfo;
struct inet_timewait_sock *tw = NULL;
struct inet_bind_hashbucket *head;
int port = inet_sk(sk)->inet_num;
struct net *net = sock_net(sk);
struct inet_bind_bucket *tb;
u32 remaining, offset;
int ret, i, low, high;
u32 index;
if (port) {
head = &hinfo->bhash[inet_bhashfn(net, port,
hinfo->bhash_size)];
tb = inet_csk(sk)->icsk_bind_hash;
spin_lock_bh(&head->lock);
if (sk_head(&tb->owners) == sk && !sk->sk_bind_node.next) {
inet_ehash_nolisten(sk, NULL);
spin_unlock_bh(&head->lock);
return 0;
}
spin_unlock(&head->lock);
/* No definite answer... Walk to established hash table */
ret = check_established(death_row, sk, port, NULL);
local_bh_enable();
return ret;
}
inet_get_local_port_range(net, &low, &high);
high++; /* [32768, 60999] -> [32768, 61000[ */
remaining = high - low;
if (likely(remaining > 1))
remaining &= ~1U;
net_get_random_once(table_perturb,
INET_TABLE_PERTURB_SIZE * sizeof(*table_perturb));
index = port_offset & (INET_TABLE_PERTURB_SIZE - 1);
offset = READ_ONCE(table_perturb[index]) + (port_offset >> 32);
offset %= remaining;
/* In first pass we try ports of @low parity.
* inet_csk_get_port() does the opposite choice.
*/
offset &= ~1U;
other_parity_scan:
port = low + offset;
for (i = 0; i < remaining; i += 2, port += 2) {
if (unlikely(port >= high))
port -= remaining;
if (inet_is_local_reserved_port(net, port))
continue;
head = &hinfo->bhash[inet_bhashfn(net, port,
hinfo->bhash_size)];
spin_lock_bh(&head->lock);
/* Does not bother with rcv_saddr checks, because
* the established check is already unique enough.
*/
inet_bind_bucket_for_each(tb, &head->chain) {
if (net_eq(ib_net(tb), net) && tb->port == port) {
if (tb->fastreuse >= 0 ||
tb->fastreuseport >= 0)
goto next_port;
WARN_ON(hlist_empty(&tb->owners));
if (!check_established(death_row, sk,
port, &tw))
goto ok;
goto next_port;
}
}
tb = inet_bind_bucket_create(hinfo->bind_bucket_cachep,
net, head, port);
if (!tb) {
spin_unlock_bh(&head->lock);
return -ENOMEM;
}
tb->fastreuse = -1;
tb->fastreuseport = -1;
goto ok;
next_port:
spin_unlock_bh(&head->lock);
cond_resched();
}
offset++;
if ((offset & 1) && remaining > 1)
goto other_parity_scan;
return -EADDRNOTAVAIL;
ok:
/* Here we want to add a little bit of randomness to the next source
* port that will be chosen. We use a max() with a random here so that
* on low contention the randomness is maximal and on high contention
* it may be inexistent.
*/
i = max_t(int, i, (prandom_u32() & 7) * 2);
WRITE_ONCE(table_perturb[index], READ_ONCE(table_perturb[index]) + i + 2);
/* Head lock still held and bh's disabled */
inet_bind_hash(sk, tb, port);
if (sk_unhashed(sk)) {
inet_sk(sk)->inet_sport = htons(port);
inet_ehash_nolisten(sk, (struct sock *)tw);
}
if (tw)
inet_twsk_bind_unhash(tw, hinfo);
spin_unlock(&head->lock);
if (tw)
inet_twsk_deschedule_put(tw);
local_bh_enable();
return 0;
}简化后
int __inet_hash_connect(struct inet_timewait_death_row *death_row,
struct sock *sk, u64 port_offset,
int (*check_established)(struct inet_timewait_death_row *,
struct sock *, __u16, struct inet_timewait_sock **))
{
struct inet_hashinfo *hinfo = death_row->hashinfo;
struct inet_timewait_sock *tw = NULL;
struct inet_bind_hashbucket *head;
int port = inet_sk(sk)->inet_num;
struct net *net = sock_net(sk);
struct inet_bind_bucket *tb;
u32 remaining, offset;
int ret, i, low, high;
u32 index;
if (port) {
head = &hinfo->bhash[inet_bhashfn(net, port,hinfo->bhash_size)];
tb = inet_csk(sk)->icsk_bind_hash;
if (sk_head(&tb->owners) == sk && !sk->sk_bind_node.next) {
inet_ehash_nolisten(sk, NULL);
return 0;
}
ret = check_established(death_row, sk, port, NULL);
return ret;
}
inet_get_local_port_range(net, &low, &high);
high++;
remaining = high - low;
net_get_random_once(table_perturb,INET_TABLE_PERTURB_SIZE * sizeof(*table_perturb));
port = low + offset;
for (i = 0; i < remaining; i += 2, port += 2) {
head = &hinfo->bhash[inet_bhashfn(net, port,hinfo->bhash_size)];
inet_bind_bucket_for_each(tb, &head->chain) {
if (net_eq(ib_net(tb), net) && tb->port == port) {
if (!check_established(death_row, sk,port, &tw))
goto ok;
goto next_port;
}
}
tb = inet_bind_bucket_create(hinfo->bind_bucket_cachep,net, head, port);
goto ok;
next_port:
}
offset++;
inet_bind_hash(sk, tb, port);
if (sk_unhashed(sk)) {
inet_sk(sk)->inet_sport = htons(port);
inet_ehash_nolisten(sk, (struct sock *)tw);
}
return 0;
}一部分一部分看。
if (port) {
head = &hinfo->bhash[inet_bhashfn(net, port,hinfo->bhash_size)];
tb = inet_csk(sk)->icsk_bind_hash;
if (sk_head(&tb->owners) == sk && !sk->sk_bind_node.next) {
inet_ehash_nolisten(sk, NULL);
return 0;
}
ret = check_established(death_row, sk, port, NULL);
return ret;
}- 判断是否绑定了端口,如果绑定则找到对应的inet_bind_hashbucket
- 判断inet_bind_hashbucket->owners是否等于当前sock和当前sock的拥有者是否只有一个,若为真则执行inet_ehash_nolisten
- 否则执行check_established
inet_ehash_nolisten
inet_ehash_nolisten代码如下,调用了inet_ehash_insert
bool inet_ehash_nolisten(struct sock *sk, struct sock *osk)
{
bool ok = inet_ehash_insert(sk, osk);
................................
}inet_ehash_insert
简化后
bool inet_ehash_insert(struct sock *sk, struct sock *osk)
{
struct inet_hashinfo *hashinfo = sk->sk_prot->h.hashinfo;
struct hlist_nulls_head *list;
struct inet_ehash_bucket *head;
bool ret = true;
sk->sk_hash = sk_ehashfn(sk);
head = inet_ehash_bucket(hashinfo, sk->sk_hash);
list = &head->chain;
if (ret)
__sk_nulls_add_node_rcu(sk, list);
return ret;
}- 调用sk_ehashfn用sk生成对应ehash对应四元组的hash赋值给sk->sk_hash
- 调用__sk_nulls_add_node_rcu插入对应hash桶
我们不考虑端口复用的情况,所以每个bucket对应的sock都是唯一的,所以不执行check_established,未指定端口则和bind中的逻辑一致,在此不多叙述,详见bind部分
最后仍然调用inet_ehash_nolisten进行ehash的插入
tcp_connect
代码如下
tcp_connect
int tcp_connect(struct sock *sk)
{
struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk);
struct sk_buff *buff;
int err;
if (inet_csk(sk)->icsk_af_ops->rebuild_header(sk))
return -EHOSTUNREACH; /* Routing failure or similar. */
tcp_connect_init(sk);
if (unlikely(tp->repair)) {
tcp_finish_connect(sk, NULL);
return 0;
}
buff = sk_stream_alloc_skb(sk, 0, sk->sk_allocation, true);
if (unlikely(!buff))
return -ENOBUFS;
tcp_init_nondata_skb(buff, tp->write_seq++, TCPHDR_SYN);
tp->retrans_stamp = tcp_time_stamp;
tcp_connect_queue_skb(sk, buff);
tcp_ecn_send_syn(sk, buff);
/* Send off SYN; include data in Fast Open. */
err = tp->fastopen_req ? tcp_send_syn_data(sk, buff) :
tcp_transmit_skb(sk, buff, 1, sk->sk_allocation);
if (err == -ECONNREFUSED)
return err;
/* We change tp->snd_nxt after the tcp_transmit_skb() call
* in order to make this packet get counted in tcpOutSegs.
*/
tp->snd_nxt = tp->write_seq;
tp->pushed_seq = tp->write_seq;
buff = tcp_send_head(sk);
if (unlikely(buff)) {
tp->snd_nxt = TCP_SKB_CB(buff)->seq;
tp->pushed_seq = TCP_SKB_CB(buff)->seq;
}
TCP_INC_STATS(sock_net(sk), TCP_MIB_ACTIVEOPENS);
/* Timer for repeating the SYN until an answer. */
inet_csk_reset_xmit_timer(sk, ICSK_TIME_RETRANS,
inet_csk(sk)->icsk_rto, TCP_RTO_MAX);
return 0;
}主要逻辑如下
int tcp_connect(struct sock *sk)
{
struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk);
struct sk_buff *buff;
int err;
buff = sk_stream_alloc_skb(sk, 0, sk->sk_allocation, true);
tcp_init_nondata_skb(buff, tp->write_seq++, TCPHDR_SYN);
tp->retrans_stamp = tcp_time_stamp;
tcp_connect_queue_skb(sk, buff);
tcp_transmit_skb(sk, buff, 1, sk->sk_allocation);
buff = tcp_send_head(sk);
inet_csk_reset_xmit_timer(sk, ICSK_TIME_RETRANS,inet_csk(sk)->icsk_rto, TCP_RTO_MAX);
}- 调用sk_stream_alloc_skb生成一个sk_buff结构体,该结构体具体看必要知识。
- 调用tcp_init_nondata_skb初始化sk_buff结构体
- 初始化tp->retrans_stamp为tcp_time_stamp,记录发送syn分包的时间
- 调用tcp_connect_queue_skb将skb放入缓存队列中
- 调用tcp_transmit_skb封装sk_buff将sk_buff传入上层,发送第一个syn包
- 调用inet_csk_reset_xmit_timer重启一个计时器,tcp_transmit_skb发送syn分包后开始计时
tcp_init_nondata_skb
tcp_init_nondata_skb主要是初始化skb,该函数将生成的序列号seq,flag(syn)复制到sk_buff->cb中
static void tcp_init_nondata_skb(struct sk_buff *skb, u32 seq, u8 flags)
{
skb->ip_summed = CHECKSUM_PARTIAL;
skb->csum = 0;
TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->tcp_flags = flags;
TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->sacked = 0;
tcp_skb_pcount_set(skb, 1);
TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->seq = seq;
if (flags & (TCPHDR_SYN | TCPHDR_FIN))
seq++;
TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->end_seq = seq;
}tcp_connect_queue_skb
tcp_connect_queue_skb将skb放入了sk->sk_write_queue队列中,在传输数据时,会从该队列中取出发送。
sk->sk_wmem_queued记录了队列里skb的总大小。
static void tcp_connect_queue_skb(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb)
{
struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk);
struct tcp_skb_cb *tcb = TCP_SKB_CB(skb);
tcb->end_seq += skb->len;
__tcp_add_write_queue_tail(sk, skb);
sk->sk_wmem_queued += skb->truesize;
}
static inline void __tcp_add_write_queue_tail(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb)
{
__skb_queue_tail(&sk->sk_write_queue, skb);
}tcp_transmit_skb
tcp_transmit_skb还是比较长的。。
tcp_transmit_skb
static int __tcp_transmit_skb(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb,
int clone_it, gfp_t gfp_mask, u32 rcv_nxt)
{
const struct inet_connection_sock *icsk = inet_csk(sk);
struct inet_sock *inet;
struct tcp_sock *tp;
struct tcp_skb_cb *tcb;
struct tcp_out_options opts;
unsigned int tcp_options_size, tcp_header_size;
struct sk_buff *oskb = NULL;
struct tcp_md5sig_key *md5;
struct tcphdr *th;
int err;
BUG_ON(!skb || !tcp_skb_pcount(skb));
tp = tcp_sk(sk);
if (clone_it) {
TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->tx.in_flight = TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->end_seq
- tp->snd_una;
oskb = skb;
if (unlikely(skb_cloned(skb)))
skb = pskb_copy(skb, gfp_mask);
else
skb = skb_clone(skb, gfp_mask);
if (unlikely(!skb))
return -ENOBUFS;
}
skb_mstamp_get(&skb->skb_mstamp);
inet = inet_sk(sk);
tcb = TCP_SKB_CB(skb);
memset(&opts, 0, sizeof(opts));
if (unlikely(tcb->tcp_flags & TCPHDR_SYN))
tcp_options_size = tcp_syn_options(sk, skb, &opts, &md5);
else
tcp_options_size = tcp_established_options(sk, skb, &opts,
&md5);
tcp_header_size = tcp_options_size + sizeof(struct tcphdr);
/* if no packet is in qdisc/device queue, then allow XPS to select
* another queue. We can be called from tcp_tsq_handler()
* which holds one reference to sk_wmem_alloc.
*
* TODO: Ideally, in-flight pure ACK packets should not matter here.
* One way to get this would be to set skb->truesize = 2 on them.
*/
skb->ooo_okay = sk_wmem_alloc_get(sk) < SKB_TRUESIZE(1);
skb_push(skb, tcp_header_size);
skb_reset_transport_header(skb);
skb_orphan(skb);
skb->sk = sk;
skb->destructor = skb_is_tcp_pure_ack(skb) ? __sock_wfree : tcp_wfree;
skb_set_hash_from_sk(skb, sk);
atomic_add(skb->truesize, &sk->sk_wmem_alloc);
/* Build TCP header and checksum it. */
th = (struct tcphdr *)skb->data;
th->source = inet->inet_sport;
th->dest = inet->inet_dport;
th->seq = htonl(tcb->seq);
th->ack_seq = htonl(rcv_nxt);
*(((__be16 *)th) + 6) = htons(((tcp_header_size >> 2) << 12) |
tcb->tcp_flags);
th->check = 0;
th->urg_ptr = 0;
/* The urg_mode check is necessary during a below snd_una win probe */
if (unlikely(tcp_urg_mode(tp) && before(tcb->seq, tp->snd_up))) {
if (before(tp->snd_up, tcb->seq + 0x10000)) {
th->urg_ptr = htons(tp->snd_up - tcb->seq);
th->urg = 1;
} else if (after(tcb->seq + 0xFFFF, tp->snd_nxt)) {
th->urg_ptr = htons(0xFFFF);
th->urg = 1;
}
}
tcp_options_write((__be32 *)(th + 1), tp, &opts);
skb_shinfo(skb)->gso_type = sk->sk_gso_type;
if (likely(!(tcb->tcp_flags & TCPHDR_SYN))) {
th->window = htons(tcp_select_window(sk));
tcp_ecn_send(sk, skb, th, tcp_header_size);
} else {
/* RFC1323: The window in SYN & SYN/ACK segments
* is never scaled.
*/
th->window = htons(min(tp->rcv_wnd, 65535U));
}
#ifdef CONFIG_TCP_MD5SIG
/* Calculate the MD5 hash, as we have all we need now */
if (md5) {
sk_nocaps_add(sk, NETIF_F_GSO_MASK);
tp->af_specific->calc_md5_hash(opts.hash_location,
md5, sk, skb);
}
#endif
icsk->icsk_af_ops->send_check(sk, skb);
if (likely(tcb->tcp_flags & TCPHDR_ACK))
tcp_event_ack_sent(sk, tcp_skb_pcount(skb), rcv_nxt);
if (skb->len != tcp_header_size) {
tcp_event_data_sent(tp, sk);
tp->data_segs_out += tcp_skb_pcount(skb);
}
if (after(tcb->end_seq, tp->snd_nxt) || tcb->seq == tcb->end_seq)
TCP_ADD_STATS(sock_net(sk), TCP_MIB_OUTSEGS,
tcp_skb_pcount(skb));
tp->segs_out += tcp_skb_pcount(skb);
/* OK, its time to fill skb_shinfo(skb)->gso_{segs|size} */
skb_shinfo(skb)->gso_segs = tcp_skb_pcount(skb);
skb_shinfo(skb)->gso_size = tcp_skb_mss(skb);
/* Our usage of tstamp should remain private */
skb->tstamp.tv64 = 0;
/* Cleanup our debris for IP stacks */
memset(skb->cb, 0, max(sizeof(struct inet_skb_parm),
sizeof(struct inet6_skb_parm)));
err = icsk->icsk_af_ops->queue_xmit(sk, skb, &inet->cork.fl);
if (unlikely(err > 0)) {
tcp_enter_cwr(sk);
err = net_xmit_eval(err);
}
if (!err && oskb) {
skb_mstamp_get(&oskb->skb_mstamp);
tcp_rate_skb_sent(sk, oskb);
}
return err;
}emmmm,简化完后一个是这么个流程...,有关sk_buff的在必要知识讲完了。
static int __tcp_transmit_skb(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb,
int clone_it, gfp_t gfp_mask, u32 rcv_nxt)
{
const struct inet_connection_sock *icsk = inet_csk(sk);
struct inet_sock *inet;
struct tcp_sock *tp;
struct tcp_skb_cb *tcb;
struct tcphdr *th;
tp = tcp_sk(sk);
inet = inet_sk(sk);
tcb = TCP_SKB_CB(skb);
tcp_header_size = tcp_options_size + sizeof(struct tcphdr);
icsk->icsk_af_ops->send_check(sk, skb);
err = icsk->icsk_af_ops->queue_xmit(sk, skb, &inet->cork.fl);
}关于icsk->icsk_af_ops->queue_xmit=ip_queue_xmit,向网络层步入
Tcp的重传
懒
Accept
源函数如下
int accept(int sockfd, struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t *addrlen);- sockfd:是一个已经通过 socket 函数创建并绑定到特定地址的监听套接字
- addr:是一个指向 struct sockaddr 类型的指针,用于存储连接的对端地址信息。
- addrlen:用于指定 addr 缓冲区的大小
accept的返回值是一个新的socket结构体。
系统调用如下
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(accept, int, fd, struct sockaddr __user *, upeer_sockaddr,
int __user *, upeer_addrlen)
{
return sys_accept4(fd, upeer_sockaddr, upeer_addrlen, 0);
}
sys_accept4源码如下
sys_accept4
SYSCALL_DEFINE4(accept4, int, fd, struct sockaddr __user *, upeer_sockaddr,
int __user *, upeer_addrlen, int, flags)
{
struct socket *sock, *newsock;
struct file *newfile;
int err, len, newfd, fput_needed;
struct sockaddr_storage address;
if (flags & ~(SOCK_CLOEXEC | SOCK_NONBLOCK))
return -EINVAL;
if (SOCK_NONBLOCK != O_NONBLOCK && (flags & SOCK_NONBLOCK))
flags = (flags & ~SOCK_NONBLOCK) | O_NONBLOCK;
sock = sockfd_lookup_light(fd, &err, &fput_needed);
if (!sock)
goto out;
err = -ENFILE;
newsock = sock_alloc();
if (!newsock)
goto out_put;
newsock->type = sock->type;
newsock->ops = sock->ops;
/*
* We don't need try_module_get here, as the listening socket (sock)
* has the protocol module (sock->ops->owner) held.
*/
__module_get(newsock->ops->owner);
newfd = get_unused_fd_flags(flags);
if (unlikely(newfd < 0)) {
err = newfd;
sock_release(newsock);
goto out_put;
}
newfile = sock_alloc_file(newsock, flags, sock->sk->sk_prot_creator->name);
if (IS_ERR(newfile)) {
err = PTR_ERR(newfile);
put_unused_fd(newfd);
sock_release(newsock);
goto out_put;
}
err = security_socket_accept(sock, newsock);
if (err)
goto out_fd;
err = sock->ops->accept(sock, newsock, sock->file->f_flags);
if (err < 0)
goto out_fd;
if (upeer_sockaddr) {
if (newsock->ops->getname(newsock, (struct sockaddr *)&address,
&len, 2) < 0) {
err = -ECONNABORTED;
goto out_fd;
}
err = move_addr_to_user(&address,
len, upeer_sockaddr, upeer_addrlen);
if (err < 0)
goto out_fd;
}
/* File flags are not inherited via accept() unlike another OSes. */
fd_install(newfd, newfile);
err = newfd;
out_put:
fput_light(sock->file, fput_needed);
out:
return err;
out_fd:
fput(newfile);
put_unused_fd(newfd);
goto out_put;
}简化后
SYSCALL_DEFINE4(accept4, int, fd, struct sockaddr __user *, upeer_sockaddr,
int __user *, upeer_addrlen, int, flags)
{
struct socket *sock, *newsock;
struct file *newfile;
int err, len, newfd, fput_needed;
struct sockaddr_storage address;
sock = sockfd_lookup_light(fd, &err, &fput_needed);
newsock = sock_alloc();
newsock->type = sock->type;
newsock->ops = sock->ops;
newfile = sock_alloc_file(newsock, flags, sock->sk->sk_prot_creator->name);
err = sock->ops->accept(sock, newsock, sock->file->f_flags);
fd_install(newfd, newfile);
}- sockfd_lookup_light寻找对应fd的socket结构体
- sock_alloc创建一个新的socket结构体
- 将newsock的type和ops都赋值为fd对应socket的type和ops
- sock_alloc_file创建一个新的文件
- 调用sock->ops->accept初始化newsock
- fd_install将新的socket结构体和新的文件建立联系
inet_accept
inet_accept主要的函数如下图
int inet_accept(struct socket *sock, struct socket *newsock, int flags)
{
struct sock *sk1 = sock->sk;
struct sock *sk2 = sk1->sk_prot->accept(sk1, flags, &err);
sock_graft(sk2, newsock);
newsock->state = SS_CONNECTED;
err = 0;
}- 调用sk1->sk_prot->accept得到一个sock结构体
- sock_graft将sock结构体和socket结构体建立联系
inet_csk_accept
struct sock *inet_csk_accept(struct sock *sk, int flags, int *err)
{
struct inet_connection_sock *icsk = inet_csk(sk);
struct request_sock_queue *queue = &icsk->icsk_accept_queue;
struct request_sock *req;
struct sock *newsk;
int error;
if (sk->sk_state != TCP_LISTEN)
goto out_err;
if (reqsk_queue_empty(queue)) {
long timeo = sock_rcvtimeo(sk, flags & O_NONBLOCK);
if (!timeo)
goto out_err;
error = inet_csk_wait_for_connect(sk, timeo);
if (error)
goto out_err;
}
req = reqsk_queue_remove(queue, sk);
newsk = req->sk;
return newsk;
}- 判断icsk_accept_queue是否为空,若为空则进入if语句,调用sock_rcvtimeo判断当前sock是否为阻塞,若为阻塞,则执行inet_csk_wait_for_connect,若不阻塞则直接返回
- 若不为空,则从队列中取出一个sock并返回
inet_csk_wait_for_connect
可以看到inet_csk_wait_for_connect里面是一个死循环,并调用了schedule_timeout判断是否超时
也调用reqsk_queue_empty判断队列是否为空
static int inet_csk_wait_for_connect(struct sock *sk, long timeo)
{
struct inet_connection_sock *icsk = inet_csk(sk);
DEFINE_WAIT(wait);
int err;
for (;;) {
prepare_to_wait_exclusive(sk_sleep(sk), &wait,
TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
release_sock(sk);
if (reqsk_queue_empty(&icsk->icsk_accept_queue))
timeo = schedule_timeout(timeo);
sched_annotate_sleep();
lock_sock(sk);
err = 0;
if (!reqsk_queue_empty(&icsk->icsk_accept_queue))
break;
err = -EINVAL;
if (sk->sk_state != TCP_LISTEN)
break;
err = sock_intr_errno(timeo);
if (signal_pending(current))
break;
err = -EAGAIN;
if (!timeo)
break;
}
finish_wait(sk_sleep(sk), &wait);
return err;
}schedule_timeout
signed long __sched schedule_timeout(signed long timeout)
{
struct timer_list timer;
unsigned long expire;
switch (timeout)
{
case MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT:
schedule();
goto out;
default:
if (timeout < 0) {
dump_stack();
current->state = TASK_RUNNING;
goto out;
}
}
expire = timeout + jiffies;
schedule();
timeout = expire - jiffies;
out:
return timeout < 0 ? 0 : timeout;
}- jiffies是内核用于记录时间的滴答数,switch什么都不执行,计算expire得出超时的时间,并且在最后计算出剩余的时间timeout 并返回
timeo每次执行schedule_timeout都会减少直到小于0导致inet_csk_wait_for_connect的死循环退出,当icsk_accept_queue队列不为空也会退出,但是err为0,不会执行inet_csk_accept的goto out_err。至于什么时候放sock到icsk_accept_queue队列中后面会讲到。
接收syn包
当一个syn包通过网络传到本机网卡,网卡会调用函数将其解封,在处理传输层的数据时会调用tcp_v4_rcv函数处理。
tcp_v4_rcv
我们主要探讨在listen状态下的sock接受到syn包,故简化成以下状态
int tcp_v4_rcv(struct sk_buff *skb)
{
struct net *net = dev_net(skb->dev);
const struct iphdr *iph;
const struct tcphdr *th;
bool refcounted;
struct sock *sk;
int ret;
th = (const struct tcphdr *)skb->data;
iph = ip_hdr(skb);
sk = __inet_lookup_skb(&tcp_hashinfo, skb, __tcp_hdrlen(th), th->source,th->dest,
&refcounted);
if (sk->sk_state == TCP_LISTEN) {
ret = tcp_v4_do_rcv(sk, skb);
goto put_and_return;
}
}- 在网络数据包沿着各层拆解完成后,各层会调用skb_pull将sk_buff->data变成指向下一层的指针,故当数据包到达tcp_v4_rcv时,sk_buff->data指向tcp的协议数据,故可以th = (const struct tcphdr *)skb->data;获取tcp的协议数据
- 调用__inet_lookup_skb用skb中的数据在hashbucket中寻找符合条件的sock并返回
- 调用tcp_v4_do_rcv
六级标题有bug,没七级标题了(悲),后面每个函数的递归就按照顺序来写把。
__inet_lookup_skb
可以看到,__inet_lookup_skb是先从ehash寻找再从bhash中寻找
static inline struct sock *__inet_lookup
(struct net *net,struct inet_hashinfo *hashinfo,struct sk_buff *skb, int doff,
const __be32 saddr, const __be16 sport,const __be32 daddr, const __be16 dport,
const int dif,bool *refcounted)
{
u16 hnum = ntohs(dport);
struct sock *sk;
sk = __inet_lookup_established(net, hashinfo, saddr, sport,daddr, hnum, dif);
*refcounted = true;
if (sk)
return sk;
*refcounted = false;
return __inet_lookup_listener(net, hashinfo, skb, doff, saddr,sport, daddr, hnum, dif);
}__inet_lookup_established
逻辑很简单,就是拿sk_buff中记录的四元组来计算hash找到对应的hash头节点,并遍历该链表找到四元组hash相同的sock,至于sk->sk_hash,早在inet_ehash_insert函数将sock插入ehash已经赋值
sk->sk_hash = sk_ehashfn(sk);
struct sock *__inet_lookup_established(struct net *net,
struct inet_hashinfo *hashinfo,
const __be32 saddr, const __be16 sport,
const __be32 daddr, const u16 hnum,
const int dif)
{
struct sock *sk;
unsigned int hash = inet_ehashfn(net, daddr, hnum, saddr, sport);
unsigned int slot = hash & hashinfo->ehash_mask;
struct inet_ehash_bucket *head = &hashinfo->ehash[slot];
begin:
sk_nulls_for_each_rcu(sk, node, &head->chain) {
if (sk->sk_hash != hash)
continue;
goto found;
}
}
found:
return sk;
}__inet_lookup_listener
至于__inet_lookup_listener,原理上和__inet_lookup_established相同,不过引入的评分机制,对于在该hash桶内的sock都会有一个评分,返回一个评分高的sock
struct sock *__inet_lookup_listener(struct net *net,
struct inet_hashinfo *hashinfo,
struct sk_buff *skb, int doff,
const __be32 saddr, __be16 sport,
const __be32 daddr, const unsigned short hnum,
const int dif)
{
unsigned int hash = inet_lhashfn(net, hnum);
struct inet_listen_hashbucket *ilb = &hashinfo->listening_hash[hash];
int score, hiscore = 0, matches = 0, reuseport = 0;
bool exact_dif = inet_exact_dif_match(net, skb);
struct sock *sk, *result = NULL;
struct hlist_nulls_node *node;
u32 phash = 0;
sk_nulls_for_each_rcu(sk, node, &ilb->nulls_head) {
score = compute_score(sk, net, hnum, daddr, dif, exact_dif);
if (score > hiscore) {
reuseport = sk->sk_reuseport;
if (reuseport) {
phash = inet_ehashfn(net, daddr, hnum,saddr, sport);
result = reuseport_select_sock(sk, phash,skb, doff);
if (result)
return result;
matches = 1;
}
result = sk;
hiscore = score;
} else if (score == hiscore && reuseport) {
matches++;
if (reciprocal_scale(phash, matches) == 0)
result = sk;
phash = next_pseudo_random32(phash);
}
}
return result;
}tcp_v4_do_rcv
tcp_v4_do_rcv前面的函数都没做什么主要看tcp_rcv_state_process
int tcp_v4_do_rcv(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb)
{
if (tcp_rcv_state_process(sk, skb)) {
rsk = sk;
goto reset;
}
return 0;
}tcp_rcv_state_process
tcp_rcv_state_process会根据skb的状态来做出不同的行为,当前sock是listen状态且当前收到的是syn包会执行icsk->icsk_af_ops->conn_request即tcp_conn_request。
int tcp_rcv_state_process(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb)
{
struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk);
struct inet_connection_sock *icsk = inet_csk(sk);
const struct tcphdr *th = tcp_hdr(skb);
struct request_sock *req;
int queued = 0;
bool acceptable;
switch (sk->sk_state) {
case TCP_LISTEN:
if (th->syn) {
acceptable = icsk->icsk_af_ops->conn_request(sk, skb) >= 0;
return 0;
}
}tcp_conn_request
tcp_conn_request代码很长,挑重要的来看
tcp_conn_request
int tcp_conn_request(struct request_sock_ops *rsk_ops,
const struct tcp_request_sock_ops *af_ops,
struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb)
{
struct tcp_fastopen_cookie foc = { .len = -1 };
__u32 isn = TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->tcp_tw_isn;
struct tcp_options_received tmp_opt;
struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk);
struct net *net = sock_net(sk);
struct sock *fastopen_sk = NULL;
struct dst_entry *dst = NULL;
struct request_sock *req;
bool want_cookie = false;
struct flowi fl;
/* TW buckets are converted to open requests without
* limitations, they conserve resources and peer is
* evidently real one.
*/
if ((net->ipv4.sysctl_tcp_syncookies == 2 ||
inet_csk_reqsk_queue_is_full(sk)) && !isn) {
want_cookie = tcp_syn_flood_action(sk, skb, rsk_ops->slab_name);
if (!want_cookie)
goto drop;
}
if (sk_acceptq_is_full(sk)) {
NET_INC_STATS(sock_net(sk), LINUX_MIB_LISTENOVERFLOWS);
goto drop;
}
req = inet_reqsk_alloc(rsk_ops, sk, !want_cookie);
if (!req)
goto drop;
tcp_rsk(req)->af_specific = af_ops;
tcp_clear_options(&tmp_opt);
tmp_opt.mss_clamp = af_ops->mss_clamp;
tmp_opt.user_mss = tp->rx_opt.user_mss;
tcp_parse_options(skb, &tmp_opt, 0, want_cookie ? NULL : &foc);
if (want_cookie && !tmp_opt.saw_tstamp)
tcp_clear_options(&tmp_opt);
tmp_opt.tstamp_ok = tmp_opt.saw_tstamp;
tcp_openreq_init(req, &tmp_opt, skb, sk);
inet_rsk(req)->no_srccheck = inet_sk(sk)->transparent;
/* Note: tcp_v6_init_req() might override ir_iif for link locals */
inet_rsk(req)->ir_iif = inet_request_bound_dev_if(sk, skb);
af_ops->init_req(req, sk, skb);
if (security_inet_conn_request(sk, skb, req))
goto drop_and_free;
if (!want_cookie && !isn) {
/* VJ's idea. We save last timestamp seen
* from the destination in peer table, when entering
* state TIME-WAIT, and check against it before
* accepting new connection request.
*
* If "isn" is not zero, this request hit alive
* timewait bucket, so that all the necessary checks
* are made in the function processing timewait state.
*/
if (tcp_death_row.sysctl_tw_recycle) {
bool strict;
dst = af_ops->route_req(sk, &fl, req, &strict);
if (dst && strict &&
!tcp_peer_is_proven(req, dst, true,
tmp_opt.saw_tstamp)) {
NET_INC_STATS(sock_net(sk), LINUX_MIB_PAWSPASSIVEREJECTED);
goto drop_and_release;
}
}
/* Kill the following clause, if you dislike this way. */
else if (!net->ipv4.sysctl_tcp_syncookies &&
(sysctl_max_syn_backlog - inet_csk_reqsk_queue_len(sk) <
(sysctl_max_syn_backlog >> 2)) &&
!tcp_peer_is_proven(req, dst, false,
tmp_opt.saw_tstamp)) {
/* Without syncookies last quarter of
* backlog is filled with destinations,
* proven to be alive.
* It means that we continue to communicate
* to destinations, already remembered
* to the moment of synflood.
*/
pr_drop_req(req, ntohs(tcp_hdr(skb)->source),
rsk_ops->family);
goto drop_and_release;
}
isn = af_ops->init_seq(skb);
}
if (!dst) {
dst = af_ops->route_req(sk, &fl, req, NULL);
if (!dst)
goto drop_and_free;
}
tcp_ecn_create_request(req, skb, sk, dst);
if (want_cookie) {
isn = cookie_init_sequence(af_ops, sk, skb, &req->mss);
req->cookie_ts = tmp_opt.tstamp_ok;
if (!tmp_opt.tstamp_ok)
inet_rsk(req)->ecn_ok = 0;
}
tcp_rsk(req)->snt_isn = isn;
tcp_rsk(req)->txhash = net_tx_rndhash();
tcp_openreq_init_rwin(req, sk, dst);
if (!want_cookie) {
tcp_reqsk_record_syn(sk, req, skb);
fastopen_sk = tcp_try_fastopen(sk, skb, req, &foc, dst);
}
if (fastopen_sk) {
af_ops->send_synack(fastopen_sk, dst, &fl, req,
&foc, TCP_SYNACK_FASTOPEN);
/* Add the child socket directly into the accept queue */
if (!inet_csk_reqsk_queue_add(sk, req, fastopen_sk)) {
reqsk_fastopen_remove(fastopen_sk, req, false);
bh_unlock_sock(fastopen_sk);
sock_put(fastopen_sk);
reqsk_put(req);
goto drop;
}
sk->sk_data_ready(sk);
bh_unlock_sock(fastopen_sk);
sock_put(fastopen_sk);
} else {
tcp_rsk(req)->tfo_listener = false;
if (!want_cookie)
inet_csk_reqsk_queue_hash_add(sk, req, TCP_TIMEOUT_INIT);
af_ops->send_synack(sk, dst, &fl, req, &foc,
!want_cookie ? TCP_SYNACK_NORMAL :
TCP_SYNACK_COOKIE);
if (want_cookie) {
reqsk_free(req);
return 0;
}
}
reqsk_put(req);
return 0;
drop_and_release:
dst_release(dst);
drop_and_free:
reqsk_free(req);
drop:
tcp_listendrop(sk);
return 0;
}在这里把一些我们不讨论的对结构体初始化的步骤删掉了,不考虑fastopen和其他错误信息
int tcp_conn_request(struct request_sock_ops *rsk_ops,const struct tcp_request_sock_ops *af_ops,struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb)
{
struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk);
struct net *net = sock_net(sk);
struct request_sock *req;
req = inet_reqsk_alloc(rsk_ops, sk, !want_cookie);
tcp_rsk(req)->af_specific = af_ops;
tcp_openreq_init(req, &tmp_opt, skb, sk);
af_ops->init_req(req, sk, skb);
inet_csk_reqsk_queue_hash_add(sk, req, TCP_TIMEOUT_INIT);
af_ops->send_synack(.........);
}- inet_reqsk_alloc创建一个request_sock 结构体。
- tcp_openreq_init用sk和skb来初始化刚才创建的req结构体
- af_ops->init_req用于初始化req的ip地址
- inet_csk_reqsk_queue_hash_add用于将req结构体放入ehash中并放入半连接队列中
- 调用af_ops->send_synack向对方发送syn+ack报文
inet_reqsk_alloc
inet_reqsk_alloc调用reqsk_alloc alloc一片空间后进行了一些赋值并初始化。
struct request_sock *inet_reqsk_alloc(const struct request_sock_ops *ops,struct sock *sk_listener,bool attach_listener)
{
struct request_sock *req = reqsk_alloc(ops, sk_listener,attach_listener);
if (req) {
struct inet_request_sock *ireq = inet_rsk(req);
ireq->ireq_state = TCP_NEW_SYN_RECV;
write_pnet(&ireq->ireq_net, sock_net(sk_listener));
ireq->ireq_family = sk_listener->sk_family;
}
return req;
}
reqsk_alloc(const struct request_sock_ops *ops, struct sock *sk_listener,bool attach_listener)
{
struct request_sock *req;
req = kmem_cache_alloc(ops->slab, GFP_ATOMIC | __GFP_NOWARN);
req->rsk_listener = NULL;
req->rsk_ops = ops;
req_to_sk(req)->sk_prot = sk_listener->sk_prot;
req->saved_syn = NULL;
return req;
}tcp_openreq_init
对req的进一步初始化,包括将源端口目的端口赋值到ireq->ir_rmt_port和ireq->ir_num
static void tcp_openreq_init(struct request_sock *req,
const struct tcp_options_received *rx_opt,
struct sk_buff *skb, const struct sock *sk)
{
struct inet_request_sock *ireq = inet_rsk(req);
req->rsk_rcv_wnd = 0; /* So that tcp_send_synack() knows! */
req->cookie_ts = 0;
tcp_rsk(req)->rcv_isn = TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->seq;
tcp_rsk(req)->rcv_nxt = TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->seq + 1;
skb_mstamp_get(&tcp_rsk(req)->snt_synack);
tcp_rsk(req)->last_oow_ack_time = 0;
req->mss = rx_opt->mss_clamp;
req->ts_recent = rx_opt->saw_tstamp ? rx_opt->rcv_tsval : 0;
ireq->tstamp_ok = rx_opt->tstamp_ok;
ireq->sack_ok = rx_opt->sack_ok;
ireq->snd_wscale = rx_opt->snd_wscale;
ireq->wscale_ok = rx_opt->wscale_ok;
ireq->acked = 0;
ireq->ecn_ok = 0;
ireq->ir_rmt_port = tcp_hdr(skb)->source;
ireq->ir_num = ntohs(tcp_hdr(skb)->dest);
ireq->ir_mark = inet_request_mark(sk, skb);
}af_ops->init_req
设置req的源目的ip地址
static void tcp_v4_init_req(struct request_sock *req,
const struct sock *sk_listener,
struct sk_buff *skb)
{
struct inet_request_sock *ireq = inet_rsk(req);
sk_rcv_saddr_set(req_to_sk(req), ip_hdr(skb)->daddr);
sk_daddr_set(req_to_sk(req), ip_hdr(skb)->saddr);
}关于抵御synflood的思路
6.17,最近在复习考研,没学啥新技术,搞了好久终于把课设搞好了,调试内核有点麻烦,有符号表的情况下不能单步调试,还要考虑多CPU多核,锁,RCU的使用,还有考虑使用内核结构体,内核版本代码标准,写了三四百行,写的不是很好还有优化的空间,这些就留给研究生的我吧。
synflood往往都会伪造源IP进行攻击,每个源IP只发送一次或多次,如果我们将第一个syn丢弃并且记录当前IP是否就可以做到降低第一次的连接率来提升可用性能。如不伪造源IP,可以记录当前IP的syn发包速率,限制在10syn包/s。
关于数据结构的选择
布隆过滤器
关于第一次syn包的记录,有什么东西是能够记录元素是否被记录,并且内存消耗还少的呢,有的喵
布隆过滤器(Bloom Filter)是1970年由布隆提出的。它实际上是一个很长的二进制向量和一系列随机映射函数。布隆过滤器可以用于检索一个元素是否在一个集合中。它的优点是空间效率和查询时间都比一般的算法要好得多,缺点是有一定的误识别率和删除困难。
我们可以创建一个位图(bitmap),相当于一连串全0的二进制位(000000000000000),对于一个IP,它存储在内存中是一个u32的类型,我们对它进行多次hash计算得到多个hash值,这些hash值我们对它取余,并在位图上将对应index的值置为1,如果我们要对其进行验证,只需要再次将IP进行相同hash操作,并在位图上验证是否都为1,若都为1则代表可能存在,若有一位不为1,则代表肯定不存在。
虽然对于百万甚至千万的流量来说有一定误报率,但是对于其本身大小以及实现难易度,可以说利大于弊。
我选择了4MB大小的位图,5个hash函数,在百万流量的情况下可以有0.005%的误报率
#define BLOOM_FILTER_BITS (1 << 22)
#define BLOOM_FUNCS 5关于hash函数,我选择了内核提供的jhash函数进行,该函数可以传入种子对同一IP生成不同的hash值,并且保证在位图上分布均匀。
size_t seeds[BLOOM_FUNCS] = {0x12345678, 0x9abcdef0, 0x13579bdf, 0x2468ace0, 0xfdb97531};
static uint32_t bloom_hash(uint32_t ip, uint32_t seed)
{
return jhash(&ip, sizeof(ip), seed) % bf->size;
}
void calu_hash(size_t ip,uint32_t arr[BLOOM_FUNCS])
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < BLOOM_FUNCS; i++) {
arr[i] = bloom_hash(ip,seeds[i]) % bf->size;
}
return;
}布隆过滤器的数据结构如下,成员不是很多(对比于一些内核结构体。。。。)
enum traffic_level {
TRAFFIC_LOW,
TRAFFIC_NORMAL,
TRAFFIC_HIGH,
TRAFFIC_ATTACK
};
struct bloom_filter {
unsigned long *bitmap;
atomic_t count;
uint32_t size;
u_int8_t funcs;
struct timer_list timer;
spinlock_t my_lock;
enum traffic_level newlevel;
enum traffic_level oldlevel;
};- bitmap:布隆过滤器的位图
- count:计时器中记录IP的数量,用于计算当前流量速率
- size:大小,用于对hash值取余操作
- funcs:使用hash函数的数量
- timer:计时器,用于在不同状况下定时清空布隆过滤器
- my_lock:自旋锁,防止条件竞争
- newlevel,oldlevel:新旧状态,只有在这两个状态不一样的情况下改变计时器的定时
初始化函数
int init_bloom(void)
{
bf = kmalloc(sizeof(*bf), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!bf)
return -ENOMEM;
spin_lock_init(&bf->my_lock);
size_t longs = BITS_TO_LONGS(BLOOM_FILTER_BITS);
bf->bitmap = kzalloc(longs * sizeof(unsigned long), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!bf->bitmap) {
kfree(bf);
return -ENOMEM;
}
atomic_set(&clear_time_ms,30000);
bf->size = BLOOM_FILTER_BITS;
bf->funcs = BLOOM_FUNCS;
atomic_set(&bf->count, 0);
bf->newlevel=TRAFFIC_LOW;
bf->oldlevel=TRAFFIC_LOW;
setup_timer(&bf->timer, clear_bloom, (unsigned long)bf);
mod_timer(&bf->timer, jiffies + msecs_to_jiffies(CLEAR_INTERVAL_MS));
return 0;
}记录和验证函数
用内核的set_bit和test_bit函数可以实现原子操作
void record_ip_into_bloom(uint32_t ip)
{
unsigned long flags;
int a;
uint32_t bloom_arr[BLOOM_FUNCS]={0};
calu_hash(ip,bloom_arr);
spin_lock_irqsave(&bf->my_lock, flags);
for(a=0;a<BLOOM_FUNCS;a++)
{
set_bit(bloom_arr[a], bf->bitmap);
}
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&bf->my_lock, flags);
return;
}
int bloom_check(uint32_t ip)
{
unsigned long flags;
int a;
uint32_t bloom_arr[BLOOM_FUNCS]={0};
calu_hash(ip,bloom_arr);
spin_lock_irqsave(&bf->my_lock, flags);
for(a=0;a<BLOOM_FUNCS;a++)
{
if (!test_bit(bloom_arr[a],bf->bitmap))
{
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&bf->my_lock, flags);
return -1;
}
}
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&bf->my_lock, flags);
return 0;
};布隆过滤器的状态转化
void change_state(void)
{
if (bf->newlevel!=bf->oldlevel)
{
switch(bf->newlevel)
{
case TRAFFIC_LOW:
atomic_set(&clear_time_ms,30000);
break;
case TRAFFIC_NORMAL:
atomic_set(&clear_time_ms,10000);
break;
case TRAFFIC_HIGH:
atomic_set(&clear_time_ms,3000);
break;
case TRAFFIC_ATTACK:
atomic_set(&clear_time_ms,1000);
break;
}
bf->oldlevel=bf->newlevel;
}
}
void check_traffic(void)
{
unsigned long flags;
size_t rate=atomic_read(&bf->count)/(atomic_read(&clear_time_ms)/1000);
if(rate<10)
{
bf->newlevel=TRAFFIC_LOW;
}
if(100<rate && rate <1000)
{
bf->newlevel=TRAFFIC_NORMAL;
}
if(1000<rate && rate<10000)
{
bf->newlevel=TRAFFIC_HIGH;
}
if(rate>10000)
{
bf->newlevel=TRAFFIC_ATTACK;
}
change_state();
}- 每当倒计时结束后用count/clear_time_ms*HZ来得到当前网络流量速率并更新下一次的清空过滤器的时间
- 只有当bf->newlevel!=bf->oldlevel才进行clear_time_ms的更新
哈希桶
受到tcp_hashinfo的启发,对于同一IP的synflood来说我们可以构造一个hash bucket记录当前IP的发包速率,并且链入hash表。
struct syn_window{
unsigned long timestamps[WINDOW_SIZE];
atomic_t count;
};
struct ip_hash_bucket
{
size_t ip;
struct syn_window syn_win;
struct hlist_nulls_node ip_node;
size_t syn_time;
atomic_t is_allow;
spinlock_t lock;
};
struct ip_hash{
struct hlist_nulls_head chain;
atomic_t count;
spinlock_t lock;
};
struct ip_hash ip_hash_buckets[hash_bucket_num];和tcp_hashinfo很像,因为就是搬过来的(。
syn_window
- timestamps:时间戳数组,用于记录每个syn包到达的时间
- count:时间戳数组元素的个数,用于判断是否刷新该数组
ip_hash_bucket
- ip:当前hash桶对应的IP。
- syn_win:用于记录当前IP发包速率的滑动窗口
- ip_node:哈希桶节点
- syn_time:最后一次接受到syn包的时间,可以根据这个删除释放节点
- is_allow:当前IP是否可以通行
- lock:自旋锁
ip_hash
- chain:链表头
- count:该哈希桶链表的个数,用于判断是否遍历该链表以摘除释放不使用的哈希桶
- lock:还是自旋锁
初始化函数
初始化每个链表的链表头,不然使用hlist_nulls_for_each_entry_rcu或hlist_nulls_for_each_entry遍历链表时会出错。设置一个定时器定时调用clear_ip_hash_buckets清空不用的哈希桶。
void init_ip_hash_buckets(void)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < hash_bucket_num; i++) {
spin_lock_init(&ip_hash_buckets[i].lock);
INIT_HLIST_NULLS_HEAD(&ip_hash_buckets[i].chain, 0);
atomic_set(&ip_hash_buckets[i].count, 0);
}
setup_timer(&bucket_timer, clear_ip_hash_buckets, (long unsigned int)0);
mod_timer(&bucket_timer, jiffies + msecs_to_jiffies(BUCKET_TIMEOUT_MS));
printk("init ip hash buckets\n");
return;
}插入和创建哈希桶
使用hlist_nulls_for_each_entry_rcu遍历链表,自动判断是否到表尾,若没初始化链表头无法自动识别表尾
size_t hash_index = jhash(&iph->saddr, sizeof(iph->saddr), seeds[0]) % hash_bucket_num;
struct ip_hash *ip_hash = &ip_hash_buckets[hash_index];
struct ip_hash_bucket *bucket=NULL;
struct hlist_nulls_node *pos;
rcu_read_lock();
hlist_nulls_for_each_entry_rcu(bucket,pos,&ip_hash->chain,ip_node) {
if (bucket->ip == iph->saddr) {
check_ip_is_allow(bucket);
if (!atomic_read(&bucket->is_allow)) {
printk("recive tcp packet from %pI4,not allow,discard the packet\n",&iph->saddr);
rcu_read_unlock();
goto discard;
}
rcu_read_unlock();
printk("recive tcp packet from %pI4,allow,handle the packet\n",&iph->saddr);
goto handle;
}
}
rcu_read_unlock();
bucket = kmalloc(sizeof(*bucket), GFP_ATOMIC);
if (!bucket) {
goto discard;
}
bucket->ip = iph->saddr;
spin_lock_init(&bucket->lock);
bucket->syn_time= jiffies;
atomic_set(&bucket->is_allow,1);
atomic_set(&bucket->syn_win.count,0);
hlist_nulls_add_head_rcu(&bucket->ip_node,&ip_hash->chain);
atomic_inc(&ip_hash->count);清除函数
根据最后一次收到syn包的时间(bucket->syn_time)判断是否超时,若超时则摘除释放该节点。记得加锁。。
void clear_ip_hash_buckets(long unsigned int a)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < hash_bucket_num; i++) {
if (!atomic_read(&ip_hash_buckets[i].count))
continue;
struct ip_hash *ip_hash = &ip_hash_buckets[i];
struct ip_hash_bucket *bucket;
struct hlist_nulls_node *pos;
spin_lock(&ip_hash->lock);
hlist_nulls_for_each_entry(bucket, pos, &ip_hash->chain, ip_node) {
if(jiffies-bucket->syn_time > BUCKET_MAX_TIME*HZ)
{
hlist_nulls_del_rcu(&bucket->ip_node);
kfree(bucket);
atomic_dec(&ip_hash->count);
}
}
spin_unlock(&ip_hash->lock);
}
mod_timer(&bucket_timer, jiffies + msecs_to_jiffies(BUCKET_TIMEOUT_MS));
printk("clear ip hash buckets\n");
return;
}判断函数
利用了滑动窗口,每次收到指定IP的包后判断win->timestamps是否满,在timestamps数组中是按照时间的先后顺序进行排序的,第一个元素进入的时间最长,若不满则判断数组中是否有超时元素,若有则移除,没有则跳过往该数组添加一个时间戳。
void check_ip_is_allow(struct ip_hash_bucket *bucket)
{
struct syn_window *win=&bucket->syn_win;
while(atomic_read(&win->count)>0 && jiffies-win->timestamps[0]>SYN_WINDOW_MAX_TIME*HZ){
memmove(&win->timestamps[0], &win->timestamps[1], (atomic_read(&win->count)-1) * sizeof(unsigned long));
atomic_dec(&bucket->syn_win.count);
}
if (atomic_read(&win->count) < WINDOW_SIZE) {
win->timestamps[atomic_read(&win->count)] = jiffies;
atomic_inc(&bucket->syn_win.count);
}
if(atomic_read(&win->count)==WINDOW_SIZE)
{
atomic_set(&bucket->is_allow,0);
printk("ip %pI4 syn times %d, time diff %ld, not allow\n",&bucket->ip,atomic_read(&win->count),jiffies-win->timestamps[0]);
}
else{
atomic_set(&bucket->is_allow,1);
printk("ip %pI4 syn times %d, time diff %ld, allow\n",&bucket->ip,atomic_read(&win->count),jiffies-win->timestamps[0]);
}
}完整代码
#define BLOOM_FILTER_BITS (1 << 22)
#define BLOOM_FUNCS 5
#define hash_bucket_num 0x100
#define WINDOW_SIZE 10
#define SYN_WINDOW_MAX_TIME 1
#define CLEAR_INTERVAL_MS 30000
#define BUCKET_MAX_TIME 3
#define BUCKET_TIMEOUT_MS 3000
size_t seeds[BLOOM_FUNCS] = {0x12345678, 0x9abcdef0, 0x13579bdf, 0x2468ace0, 0xfdb97531};
struct timer_list bucket_timer;
atomic_t clear_time_ms;
enum traffic_level {
TRAFFIC_LOW,
TRAFFIC_NORMAL,
TRAFFIC_HIGH,
TRAFFIC_ATTACK
};
struct bloom_filter {
unsigned long *bitmap;
atomic_t count;
uint32_t size;
u_int8_t funcs;
struct timer_list timer;
spinlock_t my_lock;
enum traffic_level newlevel;
enum traffic_level oldlevel;
};
void change_state(void)
{
if (bf->newlevel!=bf->oldlevel)
{
switch(bf->newlevel)
{
case TRAFFIC_LOW:
atomic_set(&clear_time_ms,30000);
break;
case TRAFFIC_NORMAL:
atomic_set(&clear_time_ms,10000);
break;
case TRAFFIC_HIGH:
atomic_set(&clear_time_ms,3000);
break;
case TRAFFIC_ATTACK:
atomic_set(&clear_time_ms,1000);
break;
}
bf->oldlevel=bf->newlevel;
}
}
void check_traffic(void)
{
unsigned long flags;
size_t rate=atomic_read(&bf->count)/(atomic_read(&clear_time_ms)/1000);
if(rate<10)
{
bf->newlevel=TRAFFIC_LOW;
}
if(100<rate && rate <1000)
{
bf->newlevel=TRAFFIC_NORMAL;
}
if(1000<rate && rate<10000)
{
bf->newlevel=TRAFFIC_HIGH;
}
if(rate>10000)
{
bf->newlevel=TRAFFIC_ATTACK;
}
change_state();
}
void clear_bloom(unsigned long data)
{
struct bloom_filter *bf = (struct bloom_filter *)data;
unsigned long flags;
if (atomic_read(&bf->count)) {
spin_lock_irqsave(&bf->my_lock, flags);
check_traffic();
size_t longs = BITS_TO_LONGS(bf->size);
memset(bf->bitmap, 0, longs * sizeof(unsigned long));
atomic_set(&bf->count, 0);
printk("clear_time_ms=%d,network state=%d\n",atomic_read(&clear_time_ms),bf->newlevel);
printk(KERN_INFO "Bloom filter cleared. Count reset to 0\n");
}
mod_timer(&bf->timer, jiffies + msecs_to_jiffies(atomic_read(&clear_time_ms)));
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&bf->my_lock, flags);
}
static uint32_t bloom_hash(uint32_t ip, uint32_t seed)
{
return jhash(&ip, sizeof(ip), seed) % bf->size;
}
int init_bloom(void)
{
bf = kmalloc(sizeof(*bf), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!bf)
return -ENOMEM;
spin_lock_init(&bf->my_lock);
size_t longs = BITS_TO_LONGS(BLOOM_FILTER_BITS);
bf->bitmap = kzalloc(longs * sizeof(unsigned long), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!bf->bitmap) {
kfree(bf);
return -ENOMEM;
}
atomic_set(&clear_time_ms,30000);
bf->size = BLOOM_FILTER_BITS;
bf->funcs = BLOOM_FUNCS;
atomic_set(&bf->count, 0);
bf->newlevel=TRAFFIC_LOW;
bf->oldlevel=TRAFFIC_LOW;
setup_timer(&bf->timer, clear_bloom, (unsigned long)bf);
mod_timer(&bf->timer, jiffies + msecs_to_jiffies(CLEAR_INTERVAL_MS));
return 0;
}
void calu_hash(size_t ip,uint32_t arr[BLOOM_FUNCS])
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < BLOOM_FUNCS; i++) {
arr[i] = bloom_hash(ip,seeds[i]) % bf->size;
}
return;
}
void record_ip_into_bloom(uint32_t ip)
{
unsigned long flags;
int a;
uint32_t bloom_arr[BLOOM_FUNCS]={0};
calu_hash(ip,bloom_arr);
spin_lock_irqsave(&bf->my_lock, flags);
for(a=0;a<BLOOM_FUNCS;a++)
{
set_bit(bloom_arr[a], bf->bitmap);
}
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&bf->my_lock, flags);
return;
}
int bloom_check(uint32_t ip)
{
unsigned long flags;
int a;
uint32_t bloom_arr[BLOOM_FUNCS]={0};
calu_hash(ip,bloom_arr);
spin_lock_irqsave(&bf->my_lock, flags);
for(a=0;a<BLOOM_FUNCS;a++)
{
if (!test_bit(bloom_arr[a],bf->bitmap))
{
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&bf->my_lock, flags);
return -1;
}
}
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&bf->my_lock, flags);
return 0;
};
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
struct syn_window{
unsigned long timestamps[WINDOW_SIZE];
atomic_t count;
};
struct ip_hash_bucket
{
size_t ip;
struct syn_window syn_win;
struct hlist_nulls_node ip_node;
size_t syn_time;
atomic_t is_allow;
spinlock_t lock;
};
struct ip_hash{
struct hlist_nulls_head chain;
atomic_t count;
spinlock_t lock;
};
struct ip_hash ip_hash_buckets[hash_bucket_num];
void clear_ip_hash_buckets(long unsigned int a)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < hash_bucket_num; i++) {
if (!atomic_read(&ip_hash_buckets[i].count))
continue;
struct ip_hash *ip_hash = &ip_hash_buckets[i];
struct ip_hash_bucket *bucket;
struct hlist_nulls_node *pos;
spin_lock(&ip_hash->lock);
hlist_nulls_for_each_entry(bucket, pos, &ip_hash->chain, ip_node) {
if(jiffies-bucket->syn_time > BUCKET_MAX_TIME*HZ)
{
hlist_nulls_del_rcu(&bucket->ip_node);
kfree(bucket);
atomic_dec(&ip_hash->count);
}
}
spin_unlock(&ip_hash->lock);
}
mod_timer(&bucket_timer, jiffies + msecs_to_jiffies(BUCKET_TIMEOUT_MS));
printk("clear ip hash buckets\n");
return;
}
void init_ip_hash_buckets(void)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < hash_bucket_num; i++) {
spin_lock_init(&ip_hash_buckets[i].lock);
INIT_HLIST_NULLS_HEAD(&ip_hash_buckets[i].chain, 0);
atomic_set(&ip_hash_buckets[i].count, 0);
}
setup_timer(&bucket_timer, clear_ip_hash_buckets, (long unsigned int)0);
mod_timer(&bucket_timer, jiffies + msecs_to_jiffies(BUCKET_TIMEOUT_MS));
printk("init ip hash buckets\n");
return;
}
void check_ip_is_allow(struct ip_hash_bucket *bucket)
{
struct syn_window *win=&bucket->syn_win;
while(atomic_read(&win->count)>0 && jiffies-win->timestamps[0]>SYN_WINDOW_MAX_TIME*HZ){
memmove(&win->timestamps[0], &win->timestamps[1], (atomic_read(&win->count)-1) * sizeof(unsigned long));
atomic_dec(&bucket->syn_win.count);
}
if (atomic_read(&win->count) < WINDOW_SIZE) {
win->timestamps[atomic_read(&win->count)] = jiffies;
atomic_inc(&bucket->syn_win.count);
}
if(atomic_read(&win->count)==WINDOW_SIZE)
{
atomic_set(&bucket->is_allow,0);
printk("ip %pI4 syn times %d, time diff %ld, not allow\n",&bucket->ip,atomic_read(&win->count),jiffies-win->timestamps[0]);
}
else{
atomic_set(&bucket->is_allow,1);
printk("ip %pI4 syn times %d, time diff %ld, allow\n",&bucket->ip,atomic_read(&win->count),jiffies-win->timestamps[0]);
}
}
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
int tcp_v4_do_rcv(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb)
{
struct sock *rsk;
const struct iphdr *iph= ip_hdr(skb);
//printk("recive tcp packet from %pI4 to %pI4\n",&iph->saddr, &iph->daddr);
if(inet_csk_reqsk_queue_len(sk) >= (sk->sk_max_ack_backlog>>1))
{
struct net *net = sock_net(sk);
struct inet_connection_sock *icsk = inet_csk(sk);
icsk->icsk_syn_retries=3;
net->ipv4.sysctl_tcp_synack_retries=3;
//printk("tcp_v4_do_rcv: backlog queue is half full, decrease synack_retries to 3\n");
}
if(bloom_check(iph->saddr)!=0)
{
//printk("recive tcp packet from %pI4,no in bloom filter,discard the first packet\n",&iph->saddr);
record_ip_into_bloom(iph->saddr);
atomic_inc(&bf->count);
goto discard;
}
printk("recive tcp packet from %pI4,In bloom filter,handle the packet and record in hash buckets\n",&iph->saddr);
size_t hash_index = jhash(&iph->saddr, sizeof(iph->saddr), seeds[0]) % hash_bucket_num;
struct ip_hash *ip_hash = &ip_hash_buckets[hash_index];
struct ip_hash_bucket *bucket=NULL;
struct hlist_nulls_node *pos;
rcu_read_lock();
hlist_nulls_for_each_entry_rcu(bucket,pos,&ip_hash->chain,ip_node) {
if (bucket->ip == iph->saddr) {
check_ip_is_allow(bucket);
if (!atomic_read(&bucket->is_allow)) {
printk("recive tcp packet from %pI4,not allow,discard the packet\n",&iph->saddr);
rcu_read_unlock();
goto discard;
}
rcu_read_unlock();
printk("recive tcp packet from %pI4,allow,handle the packet\n",&iph->saddr);
goto handle;
}
}
rcu_read_unlock();
bucket = kmalloc(sizeof(*bucket), GFP_ATOMIC);
if (!bucket) {
goto discard;
}
bucket->ip = iph->saddr;
spin_lock_init(&bucket->lock);
bucket->syn_time= jiffies;
atomic_set(&bucket->is_allow,1);
atomic_set(&bucket->syn_win.count,0);
hlist_nulls_add_head_rcu(&bucket->ip_node,&ip_hash->chain);
atomic_inc(&ip_hash->count);
handle:


Comments NOTHING